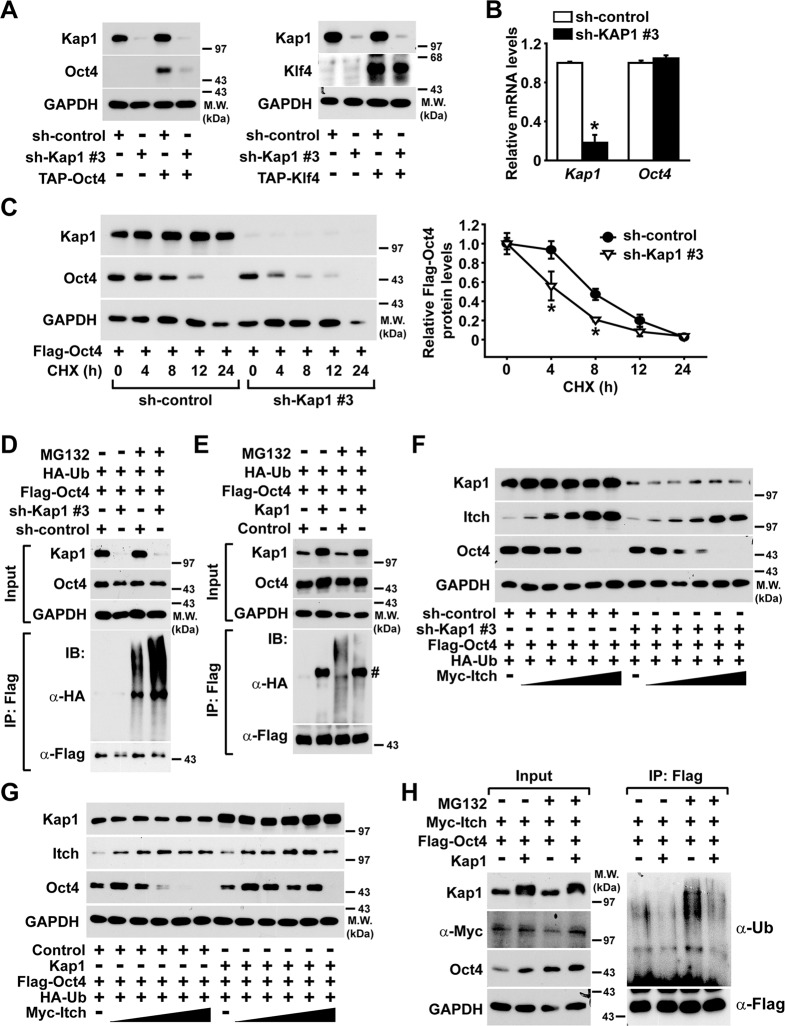
Fig. 5. The role of Kap1 on the protein stability and Itch-mediated ubiquitination of Oct4.
a The effects of Kap1 knockdown on the protein levels of transiently transfected Oct4 and Klf4 in NIH3T3 cells. NIH3T3 cells were infected with lentiviruses encoding either Kap1-specific shRNA (sh-Kap1) or control shRNA (sh-control), and expression vectors bearing TAP-Oct4 or TAP-Klf4 were transfected into the NIH3T3 cells, and followed by western blotting. b The mRNA levels of Kap1 and Oct4 were measured and normalized to those of GAPDH in the Kap1-silenced or control NIH3T3 cells. c The effects of Kap1 knockdown on the protein stability of Oct4 in NIH3T3 cells. The Kap1-silenced or control NIH3T3 cells were transiently transfected with a Flag-Oct4-expressing vector. The cells were treated with CHX for the indicated times (left panel). The protein levels of Oct4 were quantified and normalized with those of GAPDH (right panel). Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 4). d, e The effects of Kap1 knockdown or overexpression on the ubiquitination of Oct4 in NIH3T3 cells. The expression vectors bearing Flag-Oct4 and HA-Ubiquitin (Ub) were co-transfected into NIH3T3 cells in which Kap1 was silenced (d) or overexpressed (e), and the cells were treated with MG132 before immunoprecipitation with the anti-Flag antibody. f, g The effects of Kap1 knockdown or the overexpression on the Itch-mediated degradation of Oct4 in NIH3T3 cells. Flag-Oct4-expressing vector and the increasing dose of Itch-expressing vector were co-transfected into NIH3T3 cells in which Kap1 was silenced or overexpressed. h The Kap1-dependent inhibition of Itch-mediated ubiquitination of Oct4. Expression vectors bearing Flag-Oct4 or Myc-Itch were co-transfected into the control or Kap1-overexpressing NIH3T3 cells, followed by treatment with MG132 and immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody. The protein levels of Kap1, Oct4, and Itch in the immunocomplexes were determined by western blotting.