Figure 5.
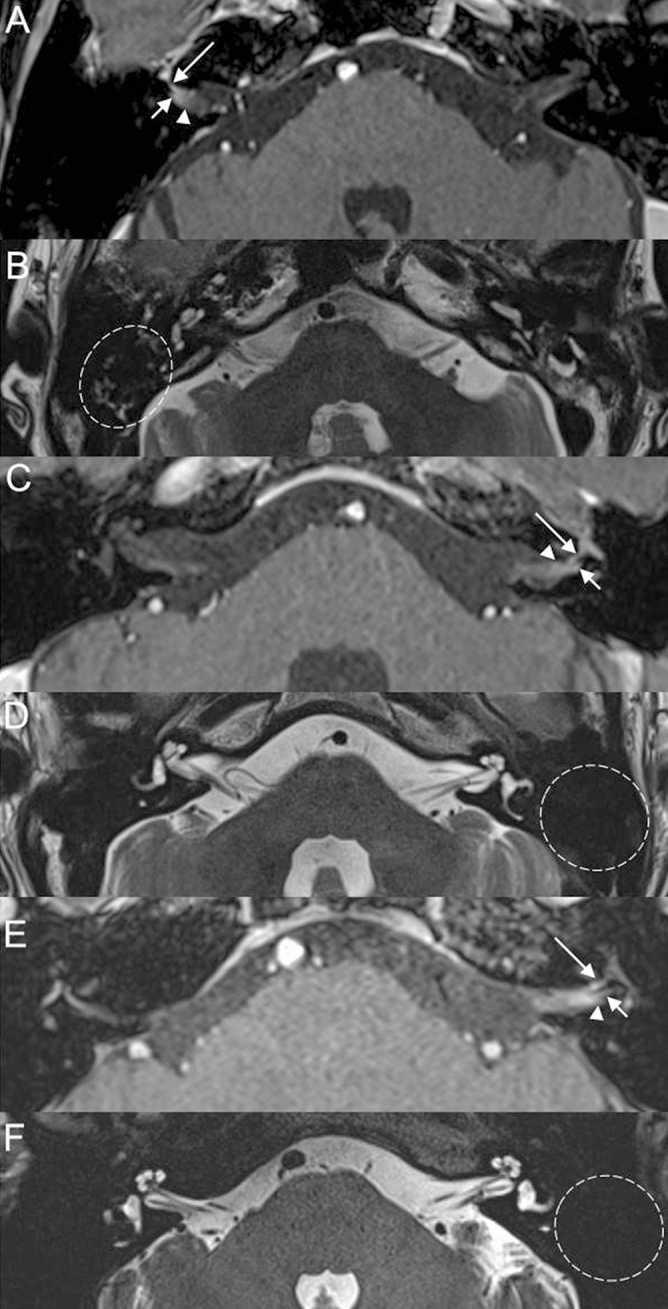
Temporal bone MRI of the patient with zoster sine herpete in the right side (A, B). (A) Post-contrast 3D T1 weighted image at the level of the internal auditory canal demonstrates enhancement of the labyrinthine segment of the right facial nerve (long arrow), right vestibular nerve (short arrow), and dura (arrowhead). (B) Non-contrast axial T2-weighted image shows high signal intensity from the fluid in the right mastoid suggesting mastoid effusion (dotted circle). Temporal bone MRI of the patient, who developed vesicular skin eruption in the left ear without acute facial nerve palsy (C, D). (C) Post-contrast 3D T1 weighted image at the level of the internal auditory canal demonstrates enhancement of the labyrinthine segment of the left facial nerve (long arrow), left vestibular nerve (short arrow), and dura (arrowhead). (D) Non-contrast axial T2-weighted image shows normal mastoid cavity on the left side (dotted circle). Temporal bone MRI of another patient, who developed vesicular skin eruption in the left ear without acute facial nerve palsy (E, F). (E) Post-contrast 3D T1 weighted image at the level of the internal auditory canal demonstrates enhancement of the labyrinthine segment of the left facial nerve (long arrow), left vestibular nerve (short arrow), and dura (arrowhead). (D) Non-contrast axial T2-weighted image shows normal mastoid cavity on the left side (dotted circle).
