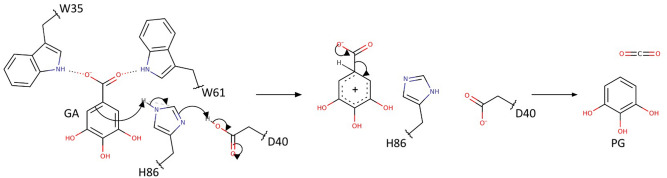
Figure 5.
The proposed catalytic mechanism for AGDC1 and PPP2. The tryptophan-clamp (W35 and W61) leads to a rotation of the substrate carboxyl group, thus increasing the energy of the substrate. The reaction proceeds via an electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr). H86, activated by D40, protonates gallate to form a Wheland intermediate. Elimination of CO2 completes the reaction by producing pyrogallol. The reaction from protocatechuic acid to catechol proceeds the same way.