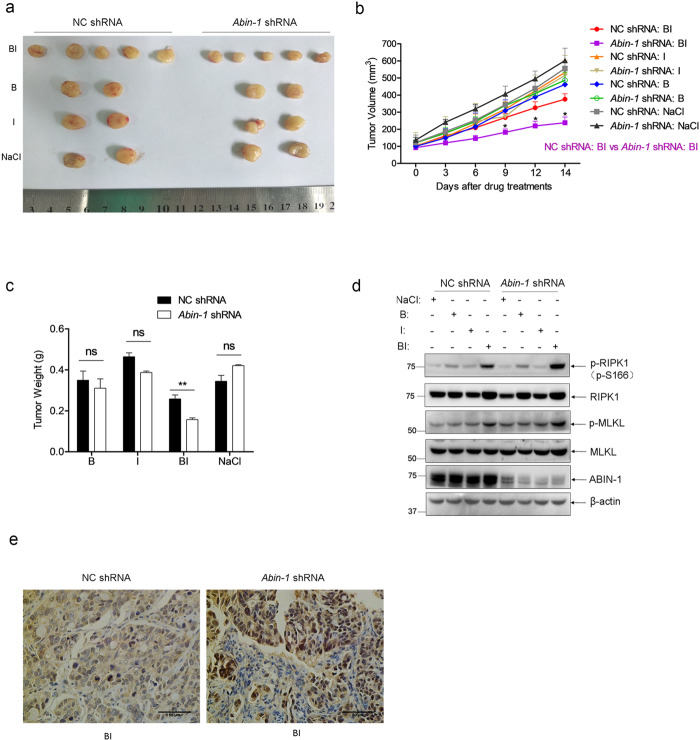
Fig. 5. ABIN-1 deficiency improves birinapant + IDN-6556-induced necroptosis cancer therapy.
HT-29 cells were transduced with lentivirus-based control shRNA (NC shRNA) or Abin-1 shRNA and screened with puromycin for 5 days to establish stable knockdown pool cells. NC shRNA cells and Abin-1 shRNA cells were subcutaneously injected into the left and right flank of BALB/c nude mice, respectively. When tumors grew to 100 mm3, mice were divided into four groups (normal saline (NaCl), n = 2; IDN-6556 (I), n = 2; birinapant (B), n = 2; birinapant + IDN-6556 (BI), n = 5). Mice were intraperitoneally injected with indicated drugs every three days. Tumor volumes were measured every 2 or 3 days, and mice were sacrificed 14 days after the first drug injection. Tumors were isolated for imaging, weighing, western blot, and immunohistochemical staining. Birinapant, 2.5 mg/kg and IDN-6556, 1.25 mg/kg. a Tumors images. b Tumor volumes. Volume (mm3) = 0.5 × length (mm) × width2 (mm2). c Tumor weights (g). d Western blot analysis for necroptosis markers. Each lane was loaded with a randomly selected tumor sample from each group. e Immunohistochemical staining with phospho-RIPK1 of tumor samples in BI group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001.