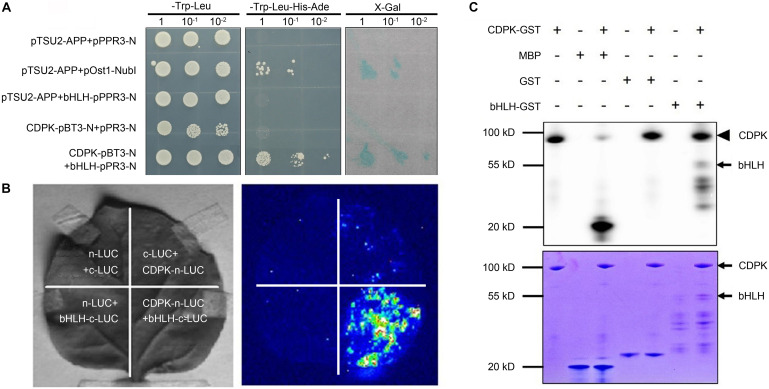
FIGURE 1.
Validation of the interaction and the probable nature between CgCDPK and CgbHLH001. (A) Identification of the interaction by Y2H assay. pTSU2-APP/pPR3-N, pTSU2-APP/bHLH-pPR3-N, CgCDPK-pBT3-N/pPR3-N: negative control; pTSU2-APP/pOst1-NubI: positive control; CDPK-pBT3-N + bHLH-pPR3-N: test group. 1, 10–1, 10–2: yeast culture dilution for 0, 10, 100 folds. (B) In vivo interaction detection by LCI assay. Left: leaves infiltrated with different agrobacterial combinations; right: LUC images corresponding to the “Left” leaves. n-LUC + bHLH-c-LUC, CDPK-n-LUC + c-LUC, n-LUC + c-LUC: negative controls; CDPK-n-LUC + bHLH-c-LUC: the test combination. (C) In vitro phosphorylation analysis. +, – on the top panel: represent the presence or absence of the components on the left; upper panel: phosphor screen result, the solid arrowhead points to the autophosphorylation band of CgCDPK, the black arrow points to the phosphorylated bands of CgbHLH001; lower panel: Coomassie brilliant blue staining, the black arrows point to the positions of CgCDPK-GST and CgbHLH001-GST proteins.