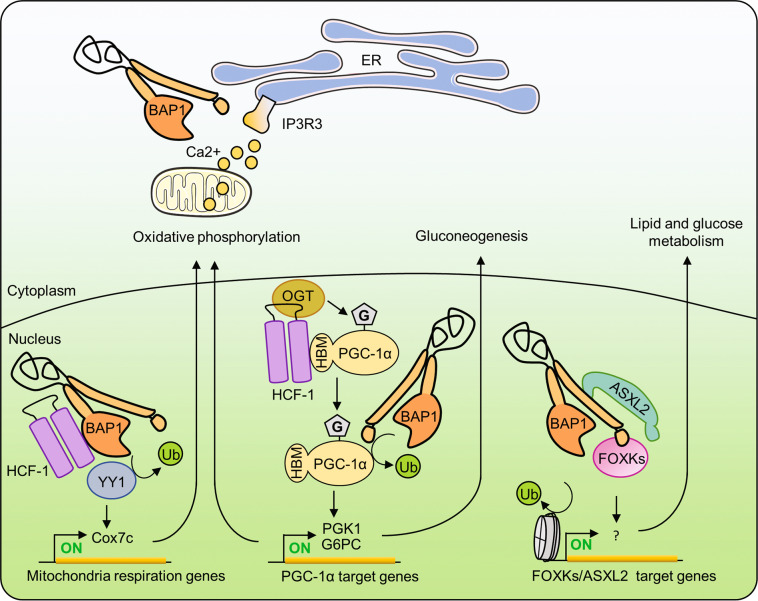
Fig. 4. Roles of the tumor suppressor BAP1 in cell metabolism.
The nuclear BAP1-HCF-1-YY1 complex regulates the expression of mitochondrial genes, thus promoting oxidative phosphorylation. ER-localized BAP1 stabilizes IP3R3 and promotes Ca2+ signaling, which might also regulate mitochondrial function. The BAP1-HCF-1-OGT complex increases the stability of PGC-1α, a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, and gluconeogenesis. PGC-1α interacts with HCF-1/OGT through its HBM motif, leading to its subsequent O-GlcNAcylation by OGT. O-GlcNAcylation of PGC-1α facilitates BAP1 recruitment, which in turn deubiquitinates PGC-1α, preventing its proteasomal degradation and thus promoting gluconeogenesis. BAP1/ASXLs/FOXKs complexes regulate several metabolic pathways. PGC-1α peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator 1α.