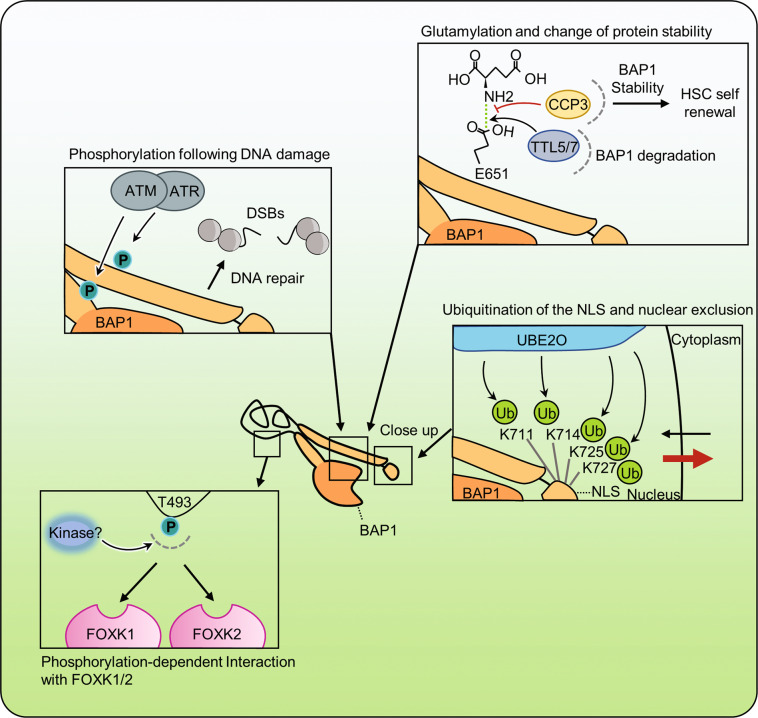
Fig. 5. Post-translational modifications regulate BAP1 functions.
BAP1 is subjected to several post-translational modifications that regulate its functions and tumor suppressor activity. Following DNA damage, ATM and ATR phosphorylate BAP1 to increase its recruitment on the site of DNA damage and allow proper DNA repair. BAP1 was also found to be targeted by glutamylation on E651. This modification is catalyzed by TTL5/7 enzymes and removed by CPP3. BAP1 glutamylation was found to be important for normal HSCs maintenance and self-renewal. Phosphorylation of T493 of BAP1 is important for its interaction with the FOXK1 and FOXK2 transcription factors. The NLS motif of BAP1 is modified by multi-monoubiquitination by the atypical E2/E3 hybrid enzyme UBE2O. NLS ubiquitination results in the retention of BAP1 in the cytoplasm. Interestingly, BAP1 deubiquitinates its own NLS domain and counteracts the effect of UBE2O. CCP3 cytosolic carboxypeptidase, TTLL5/7 tubulin tyrosine-ligase like.