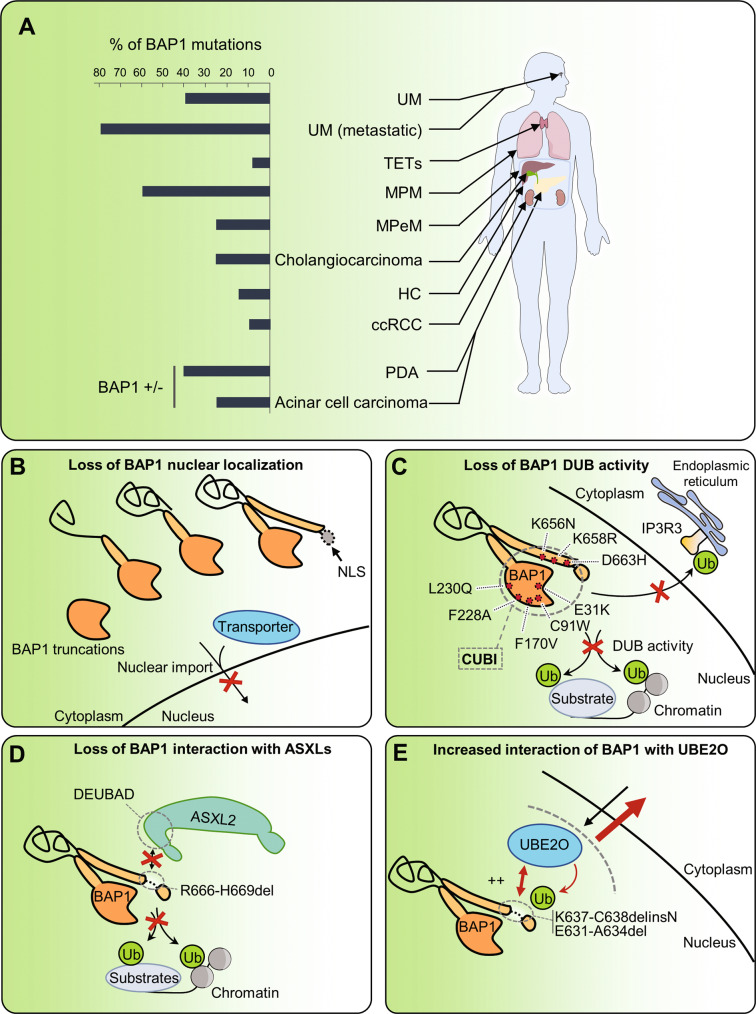
Fig. 6. Consequences of BAP1 mutations on its functions.
A Repartition of BAP1 mutations across human cancers. B Most BAP1 cancer mutations cause truncations resulting in the loss of the NLS motif, which ultimately sequesters BAP1 in the cytoplasm. C Point mutations of BAP1 can disrupt its DUB activity toward its substrates in the nucleus, notably H2AK119ub. IP3R3 receptor was recently found to be a substrate for BAP1 and disruption of BAP1 DUB activity by mutations could also alter its function in the cytoplasm. D BAP1H666-R669del mutation that specifically disrupts interaction with the ASXLs proteins required for H2AK119ub deubiquitination by BAP1. E BAP1K637-C638delinsN and BAP1E631-A634del mutants have increased interaction with UBE2O protein and, as a result, increased multi monoubiquitination of BAP1 NLS causing an overall retention of BAP1 in the cytoplasm. UM uveal melanoma, TETs thymic epithelial tumor, MPM malignant pleural mesothelioma, MPeM malignant peritoneal mesothelioma, HC hepatocellular carcinoma, ccRCC clear cell renal cell carcinoma, PDA pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, CUBI composite ubiquitin-binding interface.