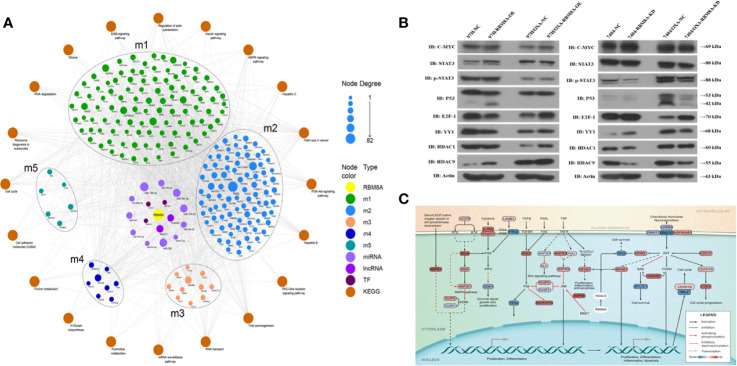
Figure 7.
Molecular network showing how RBM8A may regulate oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A) Bioinformatics analysis integrating the regulatory information of RBM8A on module genes and pivot factors to construct a comprehensive overview of RBM8A-mediated OXA resistance in HCC. In this landscape, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and transcription factors (TFs) mediate the ability of RBM8A-regulated module genes and their downstream signaling pathways to confer drug resistance on HCC cells. (B) Western blot analysis of the expression of transcription factors MYC, STAT3, P53, E2F1, YY1, HDAC1, and HDAC9 in HCC cell lines. Western blotting revealed that, after overexpression or knockdown of RBM8A in parental cell lines (PCLs) and drug-resistant (DR)-HCC cells, HDAC9 expression regulated by RBM8A was associated with OXA resistance in HCC cells. (C) Bioinformatics analysis combined with quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blotting revealed that HDAC9 is the pivotal transcription factor most closely related to the RBM8A-mediated regulation of OXA resistance in HCC. The HDAC9-module gene-KEGG signaling pathway was extracted, and the potential mechanism by which the RBM8A-HDAC9 axis regulates drug resistance in HCC was identified.