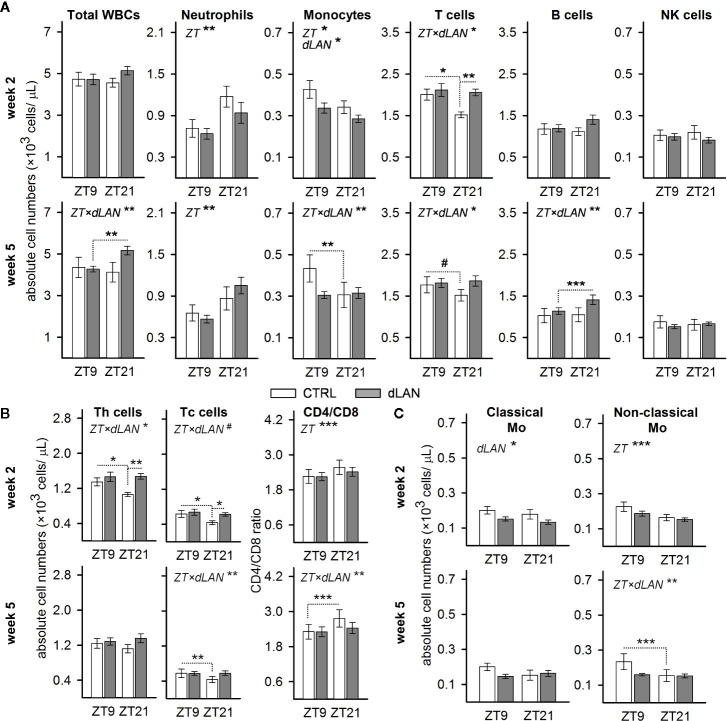
Figure 1.
Dim light at night (dLAN) disturbs the daily variation and alters the number of circulating immune cells. (A–C) Flow cytometric analysis of peripheral white blood cells (WBCs) collected at ZT9 and ZT21 from rats exposed to either the control light–dark (LD) regime (CTRL) or dLAN (~2 lx) for 2 (upper rows) and 5 (lower rows) weeks. Data represent the mean ± SEM with n = 6–9 per group. (B) Numbers of CD4+ helper (Th) and CD8+ cytotoxic (Tc) T cells and the CD4/CD8 ratio. (C) Numbers of classical (CD43loHIS48hi) and non-classical (CD43loHIS48hi) monocytes. Significant differences were evaluated by two-way repeated ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test for multiple comparisons. Only significant main effects (ZT and dLAN) or interactions (ZT×dLAN) are shown. Dotted lines indicate significant differences between individual groups if an interaction was significant. # P < 0.1, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.