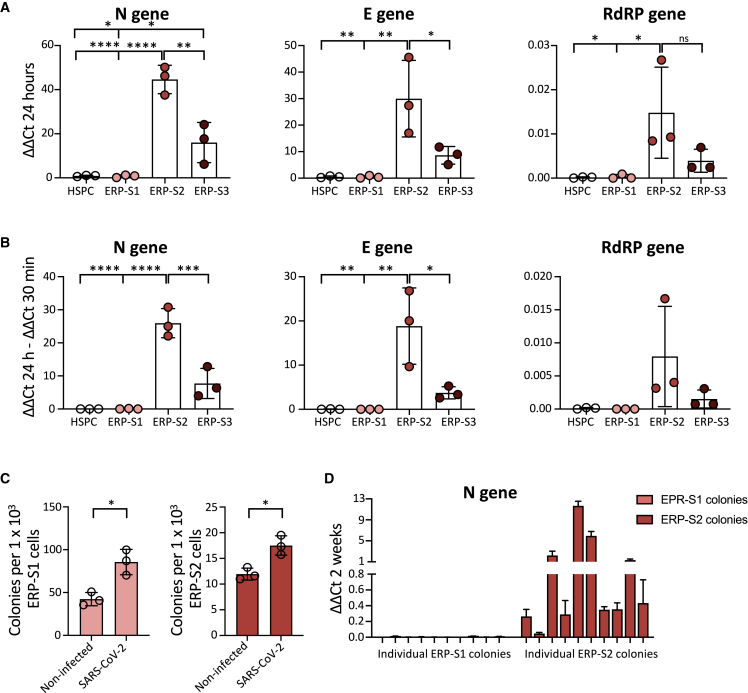
Figure 3.
SARS-CoV-2 Infects Erythroid Progenitors and can be Detected in Erythroid Colonies 14 Days Later
(A) SARS-CoV-2 infection at MOI 5 in ERPs from bone marrow. Quantification by real-time qPCR of the Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E), and RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRP) SARS-CoV-2 genes at 24 h post infection. Each dot represents an independent biological donor (n = 3). Values represent ΔΔCt normalized to GAPDH. Error bars show the mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA test was used for the comparison among the different cell populations; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns, no significance.
(B) Replication of SARS-CoV-2 genes between 30 min and 24 h post infection. Each dot represents an independent biological donor (n = 3). Values represent the differences in ΔΔCt normalized to GAPDH between the quantification of viral genes at 24 h and quantification after 30 min of viral infection. Error bars show the mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA test was used for the comparison among the different cell populations; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(C) CFU assay of ERPs after 24 h in culture with the virus. Data represent total number of colonies per 1000 ERP-S1 cells (left) or ERP-S2 cells (right); 4,000 cells of each population were seeded in triplicates in methylcellulose plates and colonies were counted 14 days later. Each dot represents an independent biological donor (n = 3). Error bars show the mean ± SD. The t test was used for the comparison between the different conditions of each sample; ∗p < 0.05.
(D) SARS-CoV-2 detection (N gene) in 10 independent colonies from ERP-S1 or ERP-S2 plates. After 14 days we pick colonies, extract RNA, and analyze by real-time qPCR the presence of the virus. Data represent the mean ± SD of the real-time qPCR triplicates for each independent colony of one experiment.