Figure 3. Inhibition of MRP1 efflux pump activity increases 14C‐APR‐246/MQ accumulation in cancer cells.
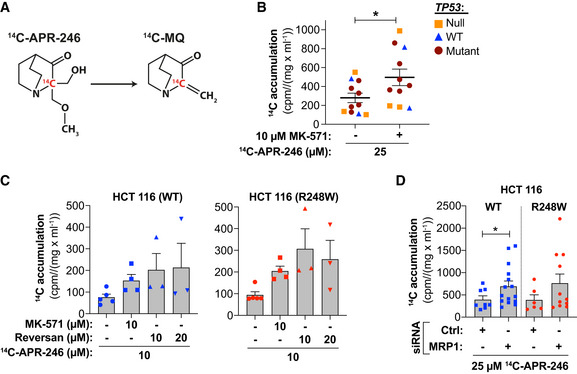
- Chemical structure of 14C ‐APR‐246 and its active product MQ.
- 14C accumulation (cpm/mg/ml) in 11 cell lines after 24 h 14C ‐APR‐246 +/− MK‐571 treatment (n ≥ 3). *P = 0.0006, paired t‐test. 14C‐accumulation and n of individual cell lines as shown in Appendix Table S3.
- 14C accumulation (cpm/mg/ml) in HCT116 (WT and R248W) cells after 24 h + treatment with 14C ‐APR‐246 +/− MK‐571 or Reversan (n ≥ 3, each dot indicates one individual experiment).
- 14C accumulation (cpm/mg/ml) in HCT116 WT and R248W cells (n ≥ 3 and ≥ 2) transfected with MRP1 siRNAs after 24 h of 14C‐APR‐246 treatment. Indicated values represent four individual MRP1 siRNAs and two individual negative control (Ctrl) siRNAs, where each dot is an individual siRNA. Mean of 14C‐accumulation after treatment and n with individual siRNA sequences is shown in Appendix Table S4. *P = 0.04 and for R248W P = 0.06, Wilcoxon matched‐pairs signed rank test.
Data information: TP53 status has been indicated. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Fig EV3, Appendix Fig S3 and Appendix Tables S3 and S4.
Source data are available online for this figure.
