FIGURE 1.
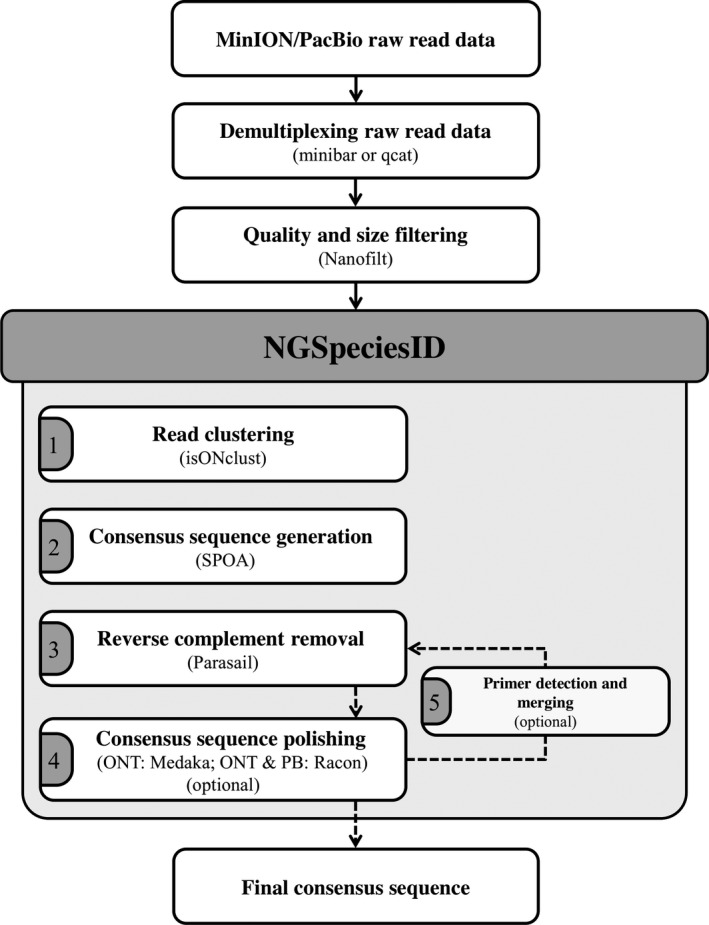
Steps involved in DNA barcode consensus calling of long‐read data. The respective software tools used in the different steps are provided in brackets. In the first step, long‐read data are usually demultiplexed. After demultiplexing, the reads are filtered for read length and quality. This step can also be carried out before demultiplexing if the respective amplicons do not differ in length. Next, consensus sequences for the individual read files can be generated using NGSpeciesID. If multiple read files need to be processed, NGSpeciesID can be run in a pipeline (see File S14). Within the tool, reads are first clustered according to similarity. Next, consensus sequences are generated for each cluster larger than an abundance threshold (default: >10% of all reads). In the third step, NGSpeciesID checks the generated consensus sequences for reverse complementary. If consensus sequences are reverse complement, then the respective clusters are merged. In step four, the consensus sequences are polished using the reads from the respective clusters (this step is optional). In the last optional step, primers can be removed if this was not already carried out by the demultiplexing or basecalling tools. If primers are removed, NGSpeciesID will carry out steps 3–4 again
