Fig. 6.
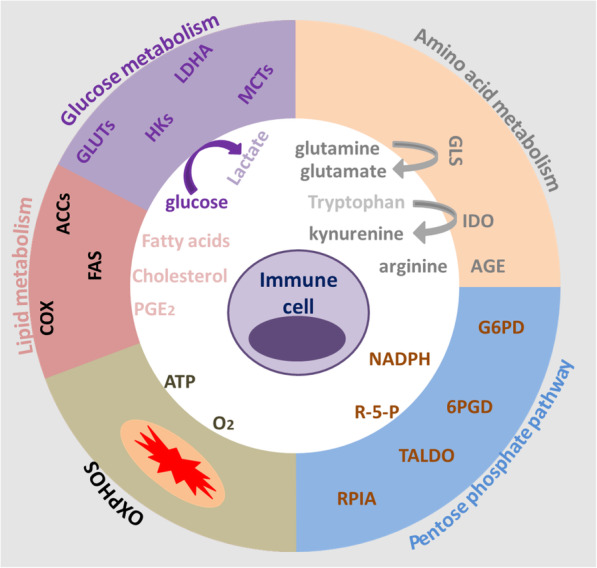
Metabolic hallmarks of immune cells and the interplay between immune cells and immune cells. Immune cells exhibit high expression of glucose transporteres (GLUT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), cyclooxygenase (COX), arginase (ARG), indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), glutaminase (GLS), and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), etc. As a consequence, glucose and the amino acids arginine, tryptophan, and glutamine are depleted from the immune microenvironment and nutrient restriction leads to an anergic status of anti-tumoral cytotoxic T cells. In addition, accelerated glycolysis by some immune cells results in lactate production and secretion via monocarboxylate-transporters (MCTs). Lactate and other metabolites, such as glutamate, prostaglandins (PGE2), kynurenines, cholesterol and R-5-P, affect immune cells
