Fig. 1. Cytokines commonly used to evaluate the inflammatory response are elevated in the rat burn model.
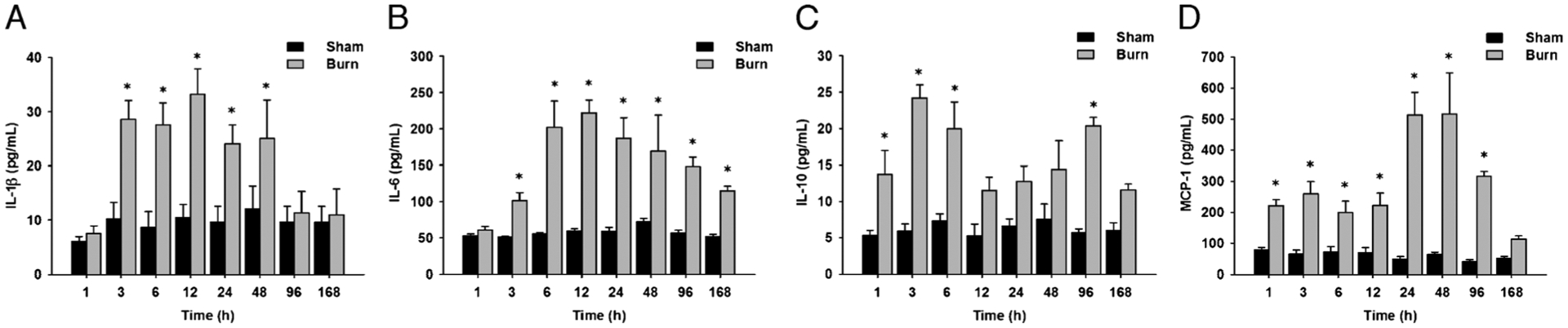
A, Serum IL-1β levels are significantly increased up to 48 days postburn compared with controls. B, Serum IL-6 levels are significantly increased up to 168 days postburn compared with controls. C, Serum IL-10 levels are significantly increased up to 96 days postburn compared with controls. D, Serum MCP-1 levels are significantly increased up to 96 days postburn compared with controls. Throughout the figure, histograms depict serum concentrations of the respective cytokine at steady-state levels. Results shown represent eight different animals per group, as indicated in the main text. Bars represent means; error bars correspond to SEM. Asterisks denote statistical significance: P < 0.05 for every comparison between groups.
