Figure 3.
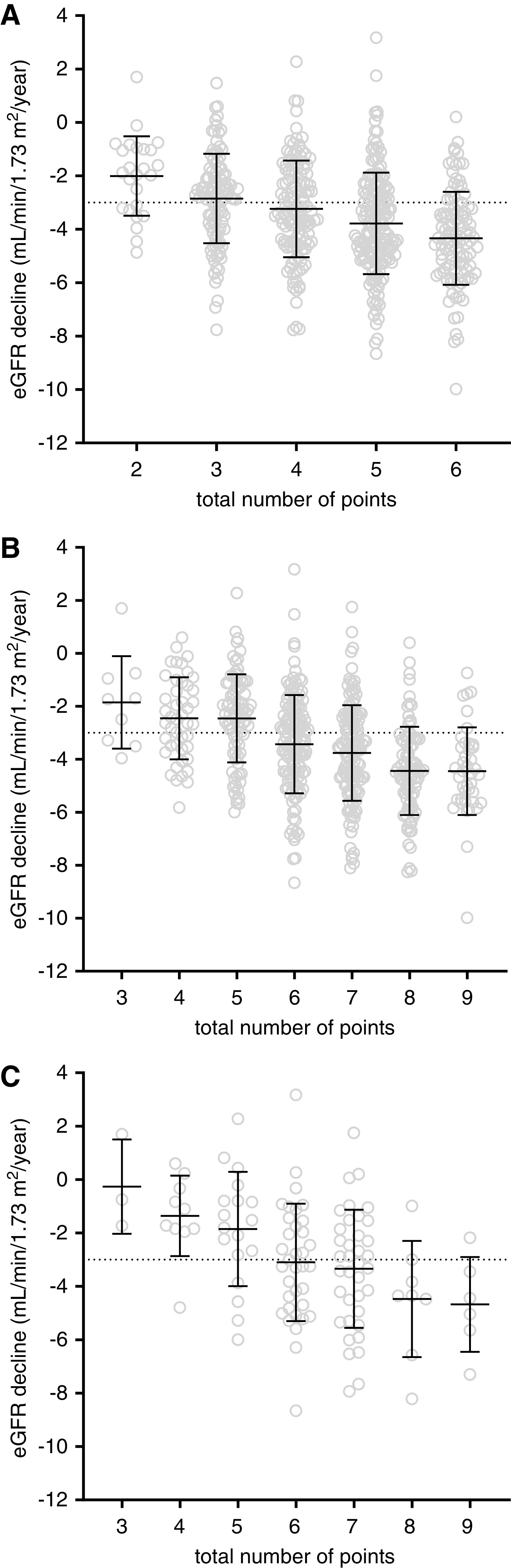
A risk score combining PKD mutation, Mayo Clinic htTKV class, and urine-to-plasma urea ratio was calculated. Rate of kidney function decline in DIPAK cohort participants (n=538), divided into risk groups according to the combined risk score of Mayo Clinic height-adjusted total kidney volume class and PKD mutation, without urine-to-plasma urea ratio (A) and the total risk score (B). Dotted line indicates division between rapidly progressive disease and moderately progressive disease (respectively below or above −3.0 ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year). Harrell C-statistics for the prediction of rapidly progressive disease was 0.68 for the risk score without the urine-to-plasma urea ratio, and 0.72 for the total risk score (P=0.007). (C) Use of the total risk score in patients with relatively early-stage disease (n=122, defined as age <40 years and eGFR>60 ml/min per 1.73 m2). The Harrell C-statistic was 0.71 in this subpopulation.
