Figure 1:
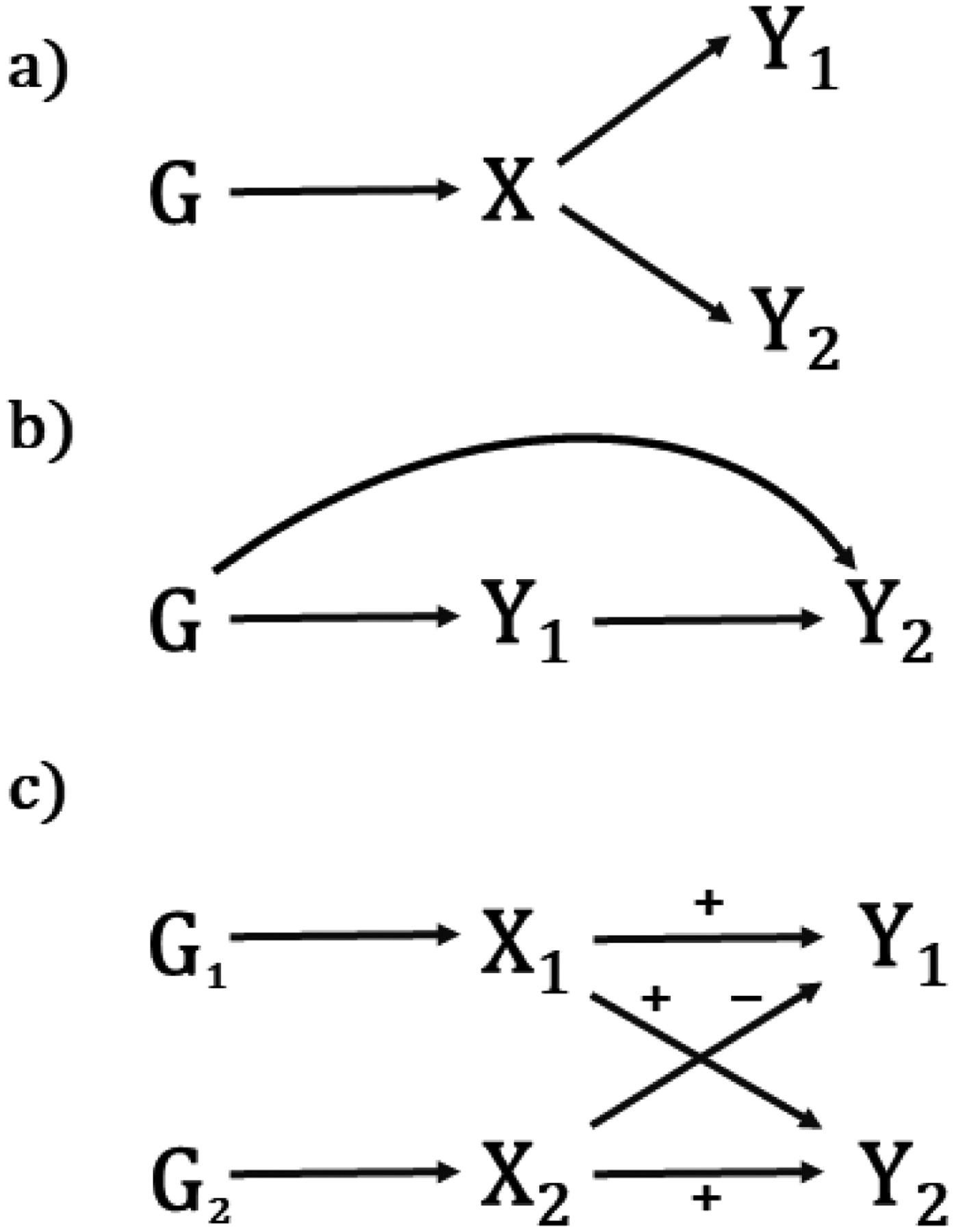
Potential sources of genetic correlation. (a) Traits Y1 and Y2 share a common cause X under genetic control. (b) Trait Y1 causes trait Y2. (c) Traits Y1 and Y2 share two common causes, X1 and X2, one of which has the same directions of effect on both traits, the other of which has opposite directions. In this case, the genome-wide genetic correlation may be close to 0, although when restricted to the loci in G1 or G2 the magnitude could be away from 0.
