Figure 1.
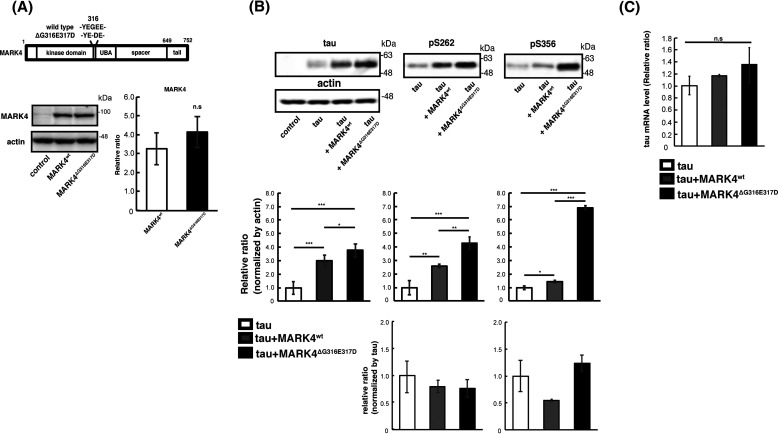
MARK4ΔG316E317D increases the level of tau to a greater extent than MARK4wt. A, (top) schematic representation of MARK4 and ΔG316E317D mutation. (bottom) MARK4wt and MARK4ΔG316E317D are expressed at similar levels in fly eyes. MARK4 expression was driven by the pan-retinal driver GMR-Gal4. Levels of MARK4wt or MARK4ΔG316E317D in fly head lysates were examined by Western blotting. Actin was used as a loading control. Representative blots (left panels) and quantification (right panels) are shown. B, coexpression of MARK4wt increased the levels of phosphorylated tau and total tau, and coexpression of MARK4ΔG316E317D increased the levels of total tau, pSer-262–tau, and pSer-356–tau in the eyes to a significantly greater extent than MARK4wt. Western blotting was performed with anti-tau antibody T46 (tau), anti-phospho–Ser-262 tau antibody (pSer-262), or anti-phospho–Ser-356 antibody (pSer-356). Representative blots (top) and quantification normalized to actin, or to total tau (bottom panels), are shown. C, coexpression of MARK4wt or MARK4ΔG316E317D does not affect tau mRNA levels. mRNA levels of tau expressed alone (tau), tau coexpressed with MARK4wt (tau+MARK4wt), and tau coexpressed with MARK4ΔG316E317D (tau+MARK4ΔG316E317D) were measured by quantitative PCR. Means ± S.D. (error bars); n = 4. n.s. (not significant), p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test).