Figure 2.
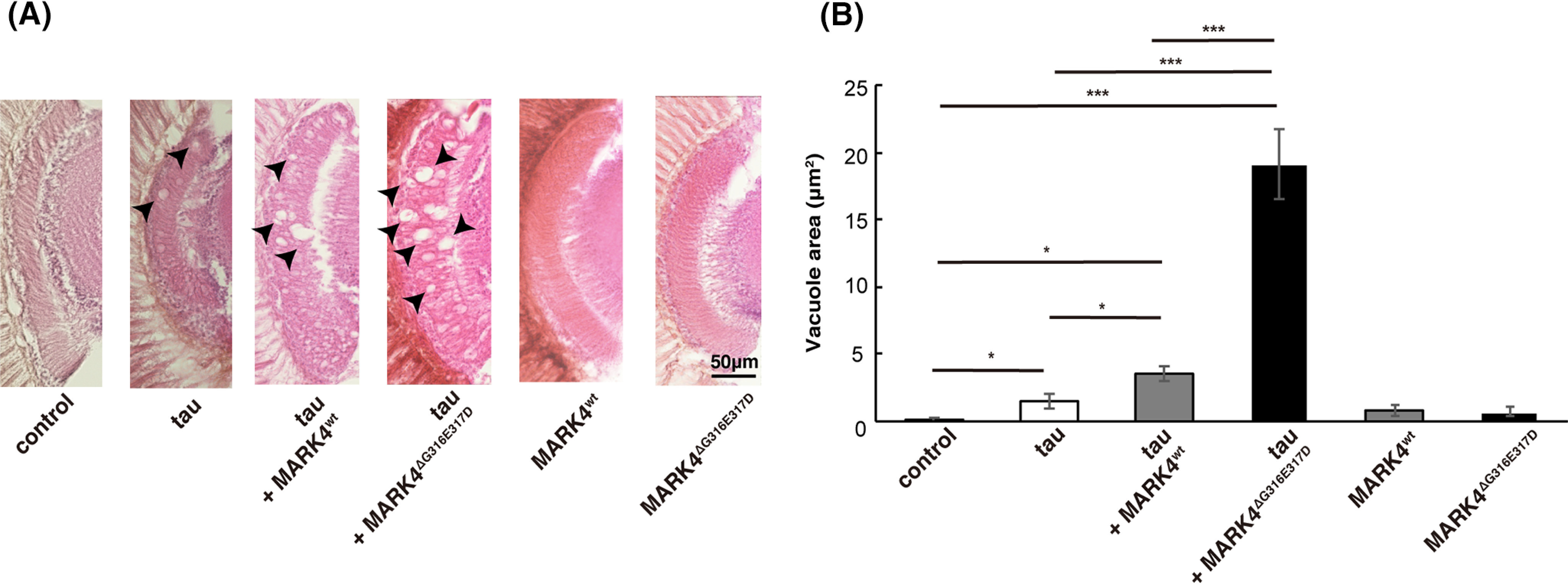
MARK4ΔG316E317D increases tau toxicity to a greater extent than MARK4wt. A, coexpression of MARK4 increased tau-induced neurodegeneration, and MARK4ΔG316E317D exerted a stronger effect than MARK4wt. Shown are lamina of flies carrying GMR-Gal4 driver alone (control), flies expressing tau (tau), flies coexpressing tau and MARK4wt (tau+MARK4wt), or flies coexpressing tau and MARK4ΔG316E317D (tau+MARK4ΔG316E317D). Expression of MARK4wt (MARK4wt) or MARK4ΔG316E317D (MARK4ΔG316E317D) alone did not cause neurodegeneration. Neurodegeneration is observed as vacuoles, indicated by arrows. B, quantification of the vacuole area. Means ± S.E. (error bars). n = 5. n.s. (not significant), p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test).
