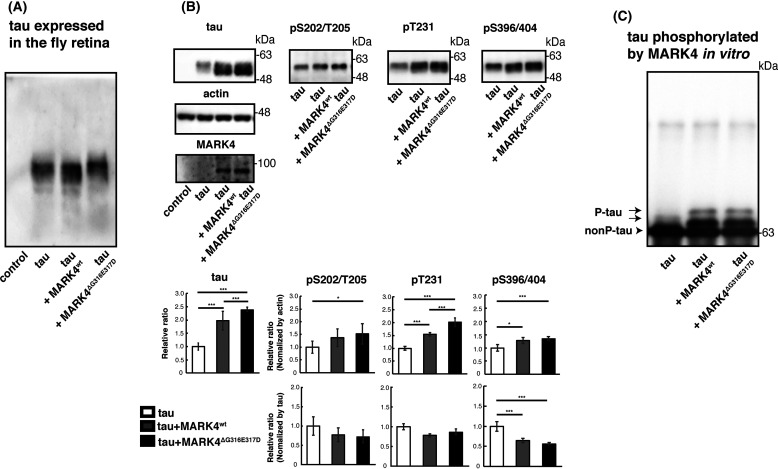
Figure 6.
Coexpression of MARK4ΔG316E317D causes accumulation of total tau and tau-phosphorylated at sites other than Ser-262/356 in vivo. A, phosphorylation profile of tau expressed alone or coexpressed with MARK4wt or MARK4ΔG316E317D in vivo. Fly head extracts were separated by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting with anti-tau antibody. Coexpression of MARK4wt increased the abundance of faster-migrating tau. By contrast, coexpression of MARK4ΔG316E317D increased the abundance of slower-migrating tau. B, Western blotting was performed using phospho-specific antibodies for SP/TP sites such as AT8 (pS202/T205), anti-pThr231 (pT231), and PHF1 (pS396/404), as well as pan-tau antibody T46 (tau). Actin was used as a loading control. Representative blots (top) and quantification (bottom panels, normalized either to actin or to total tau) are shown. Means ± S.D. (error bars); n = 4. n.s. (not significant), p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test). C, MARK4wt and MARK4ΔG316E317D phosphorylated tau in the same pattern in vitro. MARK4wt and MARK4ΔG316E317D expressed in HEK293 cells were immunoprecipitated and incubated with recombinant tau. Tau proteins were separated by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting with anti-tau antibody T46.