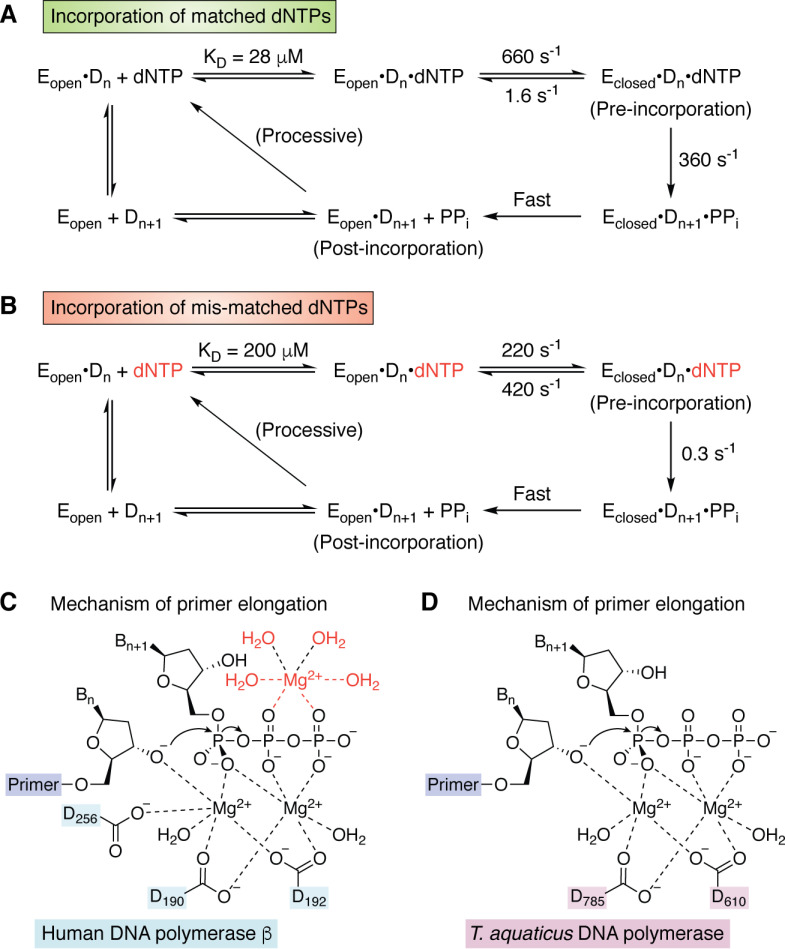
Figure 2.
A, kinetic scheme for the incorporation of matched dNTPs by T7 DNA polymerase (38, 53). When the incoming dNTP is correct, the enzyme undergoes a rapid conformational change from the open to closed form of the pre-incorporation complex. B, kinetic scheme for the incorporation of mis-matched dNTPs by T7 DNA polymerase (38, 53). When the incoming dNTP is incorrect, the rate constant for the chemical step becomes smaller than that for the conformational change back to the open form of the pre-incorporation complex. C, chemical mechanism of primer elongation for the 2-Mg (54) and 3-Mg models (55). The location of the third Mg2+ ion together with its water ligands is shown in red. Residue numbering is for human DNA polymerase β. D, chemical mechanism of primer elongation in the active site of T. aquaticus DNA polymerase, which lacks one of the carboxylate ligands present in human DNA polymerase β.