Figure 5.
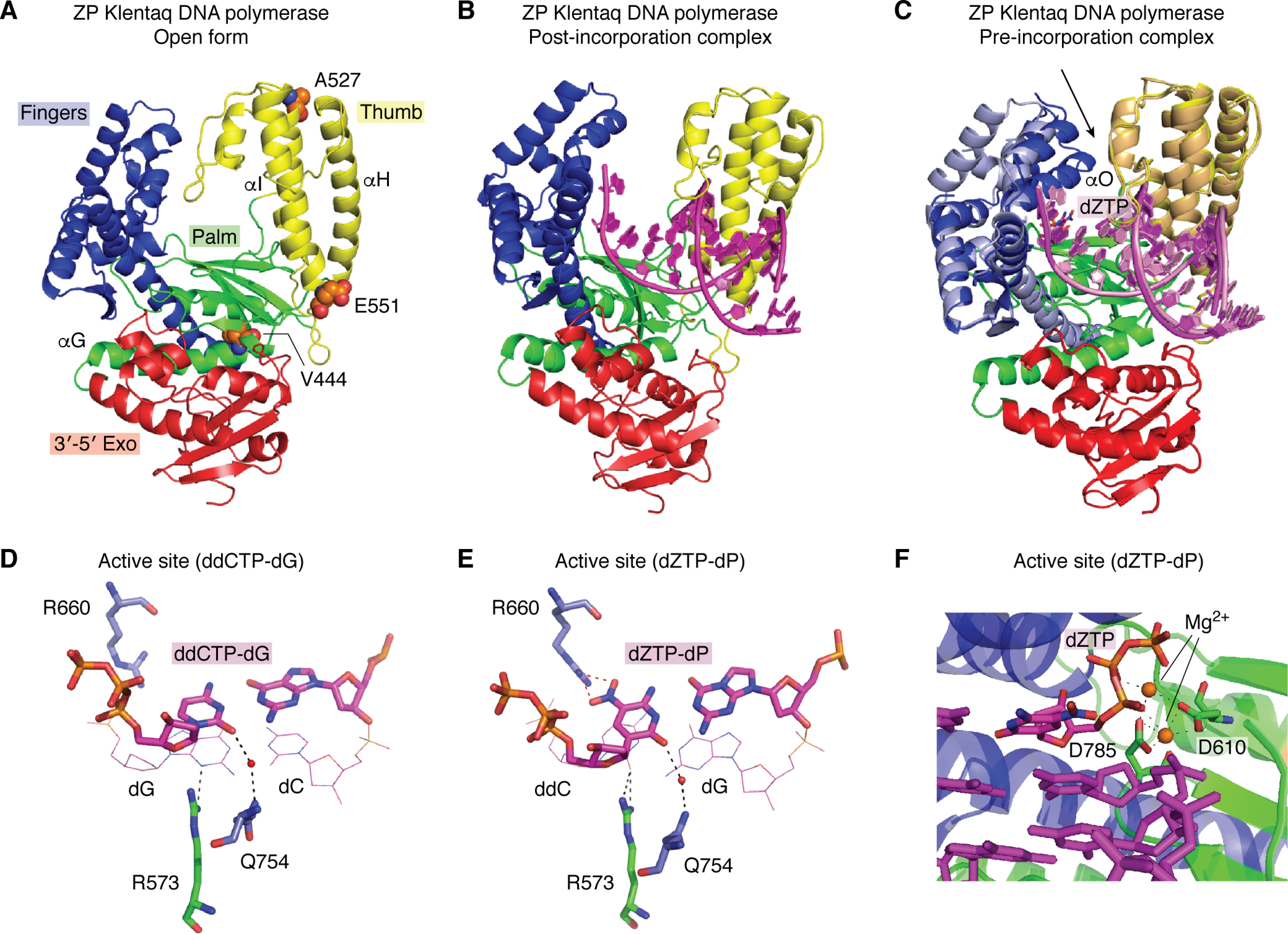
Structural properties of Klentaq DNA polymerase. A, the open form of ZP Klentaq (from PDB entry 5W6Q), shown in a cartoon rendering, includes fingers (blue), palm (green), thumb (yellow), and 3′–5′ exonuclease (red) domains. This architecture is conserved in all family A polymerases. Variant amino acid substitutions are shown as sphere models (orange, carbon; blue, nitrogen; red, oxygen), M444V, P527A, and D551E. (The fourth amino acid substitution, E832V, is disordered in the structures). α-Helices G, H, and I contribute to dynamic motion in ZP Klentaq. B, a similar rendering of ZP Klentaq in the binary, post-incorporation complex (PDB entry 5W6Q) is shown with template-primer, including P:Z in the active site (magenta cartoon rendering). C, the pre-incorporation complex of ZP Klentaq (PDB entry 5W6K) is shown superimposed on the post-incorporation complex from B. The black arrow indicates the most significant conformational change associated with the fingers domain (light blue for the initial and post-incorporation and blue for the pre-incorporation complex). The O helix closes down, forming the active site in the ternary complex with bound dZTP (magenta stick rendering). The thumb domains show a slight shift in position (light orange for post-incorporation and yellow for pre-incorporation complex). The palm and exonuclease domains show no significant differences in overall position in the two complexes. The substrate nucleic acid is shown as a cartoon rendering (pink in the post-incorporation and magenta in the post-incorporation complex). Close-ups of hydrogen-bonding interactions in the active site for the WT Klentaq bound to ddCTP-dG and dZTP-dP are shown in D and E, respectively. In each case, the dNTP is positioned through a water-mediated hydrogen-bonding interaction involving O2 (minor groove edge of the nucleobase) with Gln-754. Similarly, the penultimate primer nucleobase presents either N3 or O2 for hydrogen-bonding to Arg-573 (again a minor groove interaction). In the case of the ZP Klentaq ternary complex (E), Arg-660 hydrogen-bonds to the NO2 group present on the major groove edge of Z. F, the active site including template-primer and dZTP (magenta stick rendering), Mg2+ ions (orange spheres), and coordinating residues Asp-610 and Asp-785 (green stick rendering) are shown with a ribbon rendering of the enzyme, palm in green and fingers in blue.
