Figure 5.
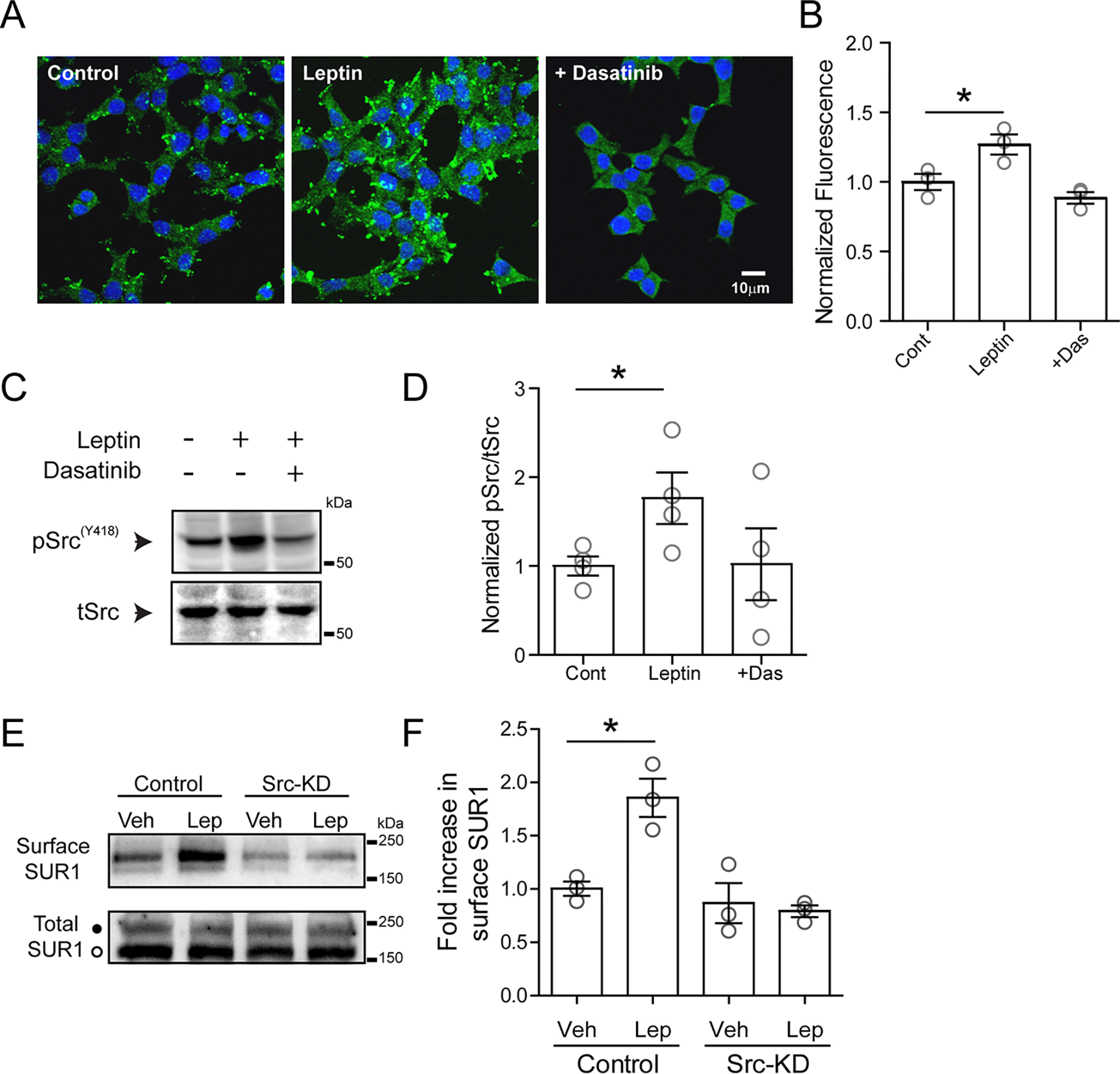
Leptin induces activation of Src kinase. A, immunofluorescence images of cultured INS-1 831/13 cells stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue) and phosphorylated SrcY418 (green) for conditions indicated. Cells were treated with vehicle (control), leptin (10 nm, 10 min), or leptin with dasatinib (25 μm, pretreated for 30 min before leptin was applied). B, group data for phosphorylated SrcY418 fluorescence for each condition normalized to the control (n = 100 cells/condition for each experiment, and the experiment was repeated three times). *, p < 0.05, unpaired Student's t test. C, representative Western blotting of phosphorylated SrcY418 from cell lysates prepared from INS-1 832/13 cells treated with vehicle, leptin, or leptin co-applied with dasatinib. D, group data from four independent experiments as indicated in C. *, p < 0.05, unpaired Student's t test. E, top, Western blotting showing surface SUR1 in response to vehicle or leptin using control cells and cells transfected with an Src kinase–dead mutant (Src-KD). Bottom, total SUR1 showing both the complex glycosylated form (top band, solid circle) that can traffic to the cell surface and the core-glycosylated form (bottom band, open circle) that is in the endoplasmic reticulum/early Golgi. F, quantitation of three independent surface SUR1 experiments. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (p = 0.0019, F = 12.95) followed by a post hoc Dunnett's multiple-comparison test with significance set to p < 0.05 (*). Error bars, S.E.
