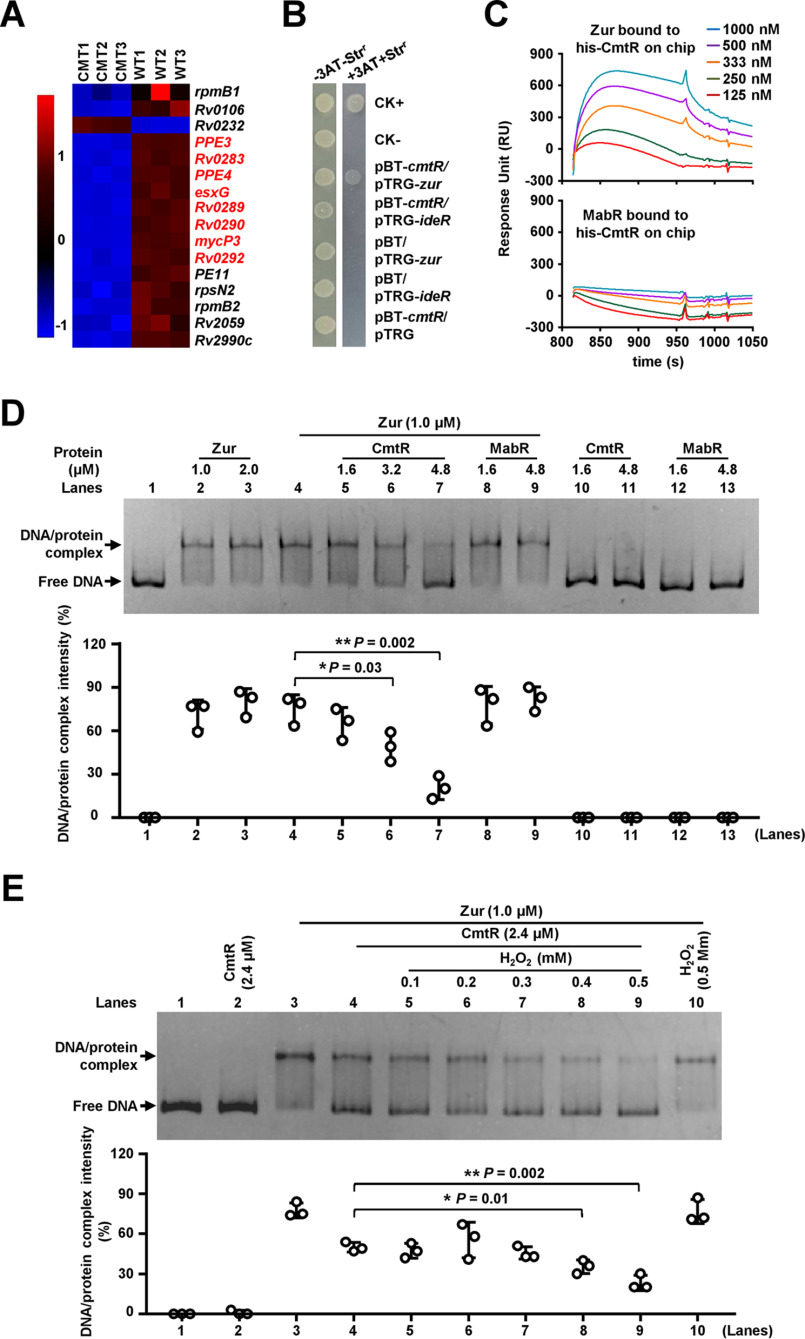
Figure 4.
Assays for studying the interaction between CmtR and Zur. A, heat map of the CmtR-regulated differential expression profile of Zur-targeted genes. CMT1, CMT2, and CMT3 represent three biological replicates of the genes in the cmtR knockout strain. WT1, WT2, and WT3 represent three biological replicates of the genes in the WT strain. B, bacterial two-hybrid assays for the interaction between CmtR and Zur. E. coli reporter strains with various recombinant plasmids were spotted on the plate in the presence or absence of streptomycin (str) and 3-amino-1, 2, 4-triazole. ideR was used as a negative control. C, SPR assays for studying the specific interaction between CmtR and Zur. For studying the interaction between Zur and CmtR, His-tagged CmtR proteins were immobilized onto the NTA chips. Zur (top panel) protein and control MabR proteins (bottom panel) at different concentrations were passed over the chip. D, EMSA for studying the inhibitory effect of CmtR on the DNA-binding activity of Zur. The rv0280p DNA substrate was co-incubated with corresponding quantities of Zur (lanes 2–4), CmtR (lanes 10 and 11), or both (lanes 5–7). MabR was used as a negative control regulator. E, EMSA for studying the effect of H2O2 on the DNA-binding activity of Zur in the presence of CmtR. Error bars represent the S.D. from three independent experiments. The P-values of the data were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test using GraphPad Prism 7. Asterisks represent significant difference (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, two-tailed Student's t test) between two groups.