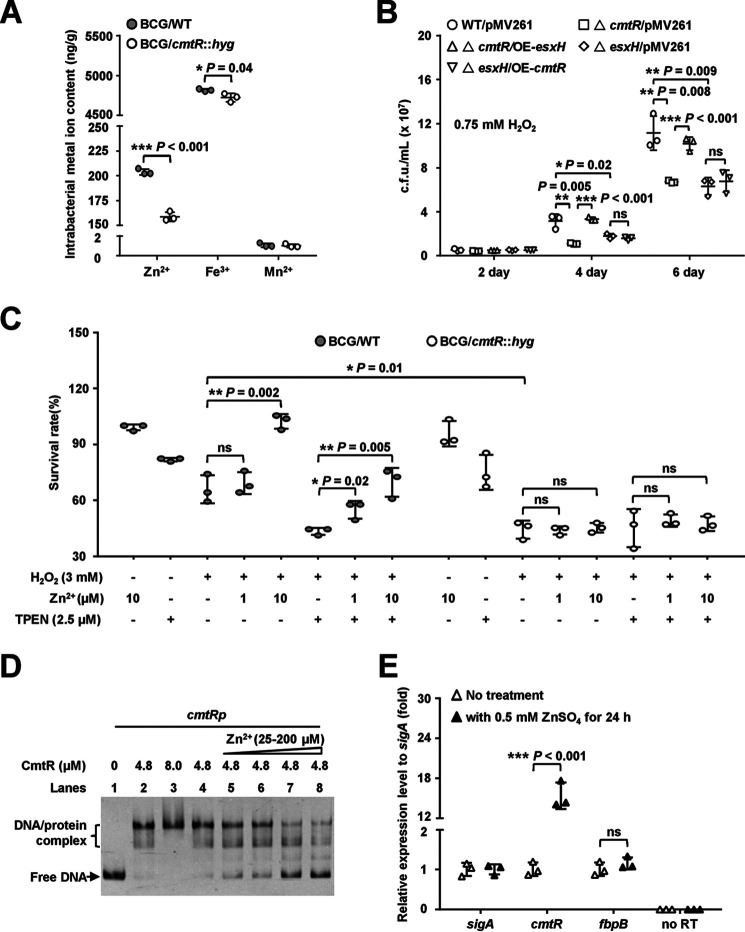
Figure 6.
Assays for studying the effect of CmtR on intracellular metal ion accumulation in bacteria and mycobacterial growth under oxidative stress. A, ICP-OES assay for measuring the intracellular metal ion contents of WT and cmtR-deleted strains of M. bovis BCG under 5 mm H2O2 stress. B, assays for studying the effects of esxH-dependent regulation of cmtR on the growth of M. bovis BCG strain under 0.75 mm H2O2 stress. WT/pMV261 represents the BCG/pMV261 strain; △cmtR/pMV261 represents the BCG cmtR::hyg/pMV261 strain; △cmtR/OE-esxH represents the BCG cmtR::hyg/pMV261-esxH strain; △esxH/pMV261 represents the BCG esxH::hyg/pMV261 strain; △esxH/OE-cmtR represents the BCG esxH::hyg/pMV261-cmtR strain. C, assays for studying the essential role of CmtR in the enhancement of exogenous Zn2+ on antioxidant ability of M. bovis BCG strains. The cmtR-deleted and WT strains were cultured in Sauton's medium till the A600 value reached 0.5, and the culture was then supplemented with or without Zn2+, the Zn2+ chelator N, N, N′, N′-tetrakis (2-pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine), and H2O2 for 24 h. D, EMSA for studying the effects of Zn2+ on the DNA-binding activity of CmtR. The cmtRp DNA substrate was co-incubated with CmtR in the absence (lanes 1–4) or presence of Zn2+ (25-200 μm) (lanes 5–8). E, qRT-PCR assays for studying the induction of cmtR expression in M. bovis BCG strain by Zn2+. Error bars represent the S.D. from three biological experiments. The P-values of the data were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test using GraphPad Prism 7. Asterisks represent significant difference (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant; two-tailed Student's t test) between two groups.