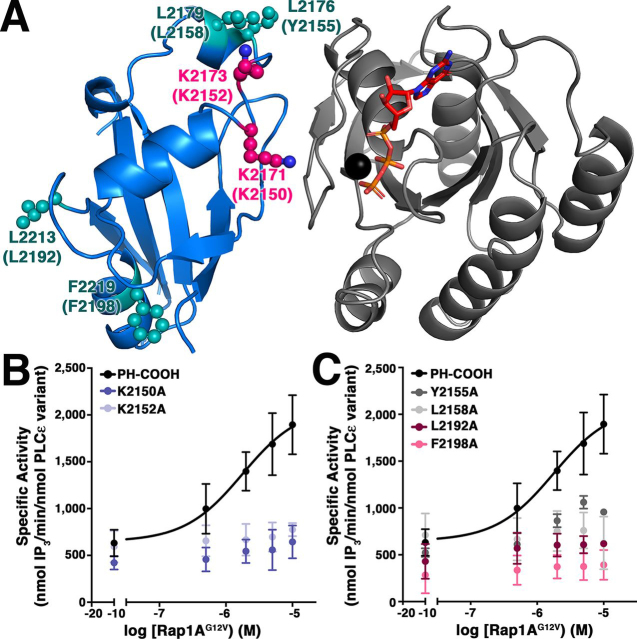
Figure 2.
Hydrophobic residues on the surface of the RA2 domain are critical for activation.A, the structure of H-Ras (gray) bound to the RA2 domain (blue, PDB entry 2C5L (14)) reveals conserved, hydrophobic residues (teal spheres) involved in crystal lattice contacts. Lys2171 and Lys2173 (hot pink spheres) were previously reported to be required for Rap1A-dependent activation. R. norvegicus residues are in parentheses. GTP is shown as orange sticks, and Mg2+ is shown as a black sphere. B and C, mutation of the Lys2150 or Lys2152 to alanine eliminates activation by Rap1AG12Vin vitro (B), as does mutation of the conserved hydrophobic residues distant from the Rap1A binding surface (C).