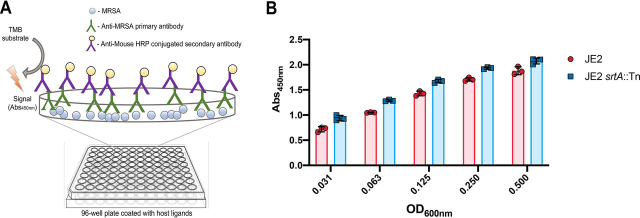
Figure 1.
An ELISA-based approach for the large-scale profiling of Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to host ligands.A, schematic diagram of the high-throughput S. aureus adhesion assay. B, recognition of surface-adhered MRSA USA300 by the primary antibody is not dependent on the presence of cell wall-anchored proteins. A Nunc™ MaxiSorp™ microtiter plate was coated with MRSA USA300 JE2 and isogenic JE2 srtA::Tn (devoid of CWAs) propagated to an OD600nm of 0.6. The cells were harvested, washed, and standardized to the various optical densities shown. Using the described ELISA, detection of surface adhered JE2 srtA::Tn was equivalent to that of the parental strain, indicating that recognition by the primary antibody is independent of CWA surface proteins. The values shown are the average mean ± S.D. of three duplicate biological replicates.