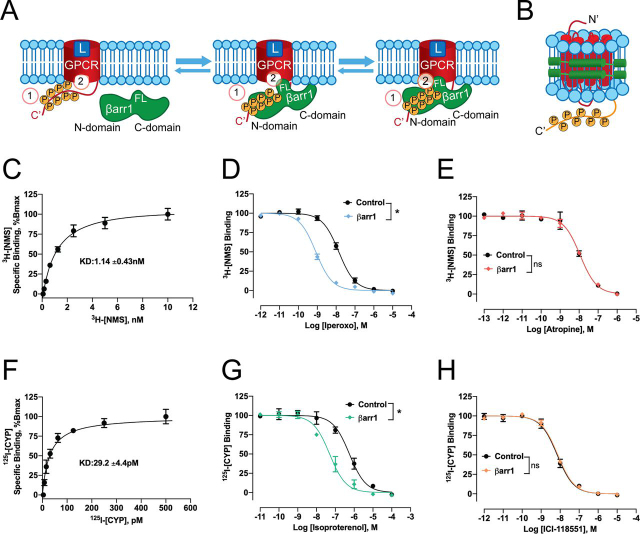
Figure 1.
Pharmacological characterization of M2V2 and β2V2 reconstituted in lipid nanodiscs: ligand binding and allosteric coupling of βarr1.A, schematic representation of GPCR–β-arrestin1 binding: βarr1 recruitment begins with binding to the phosphorylated receptor tail (1) and is followed by the engagement with the receptor core (2). C-edge loops of active βarr1 anchor it to the membrane (L, ligand; FL, finger loop). B, schematic representation of chimeric M2 muscarinic (M2V2) and β2-adrenergic (M2V2) receptors reconstituted in HDL particles (lipid nanodiscs). A synthetic phosphopeptide mimicking a phosphorylated C-terminal tail of V2 receptor was ligated to the receptors' C termini using sortase. The receptor is colored in red, the phosphorylated C-tail of V2 receptor is shown in yellow, MSP1D1E3 is shown in green. C, [3H]NMS saturation ligand binding at HDL-M2V2. D and E, competition ligand binding assays using [3H]NMS (1 nm) at HDL-M2V2 and a dose of agonist iperoxo (D) or antagonist atropine (E) in the absence (control) or presence of 1 μm βarr1. F,125I-CYP saturation ligand binding at HDL-β2V2. G and H, competition ligand binding assays using 125I-CYP (60 pm) at HDL-β2V2 and a dose of agonist isoproterenol (G) or antagonist ICI-118551 (H) in the absence (control) or presence of 1 μm βarr1. C–H, points in respective curves represent mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. Asterisks (*) in B and E indicate significant difference in IC50 values between control versus βarr1 competition curves (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post test).