Fig. 4. Bilateral optogenetic Pf-STN terminal and cell body excitation in bilateral 6-OHDA parkinsonian mice rescue akinesia and promote locomotion.
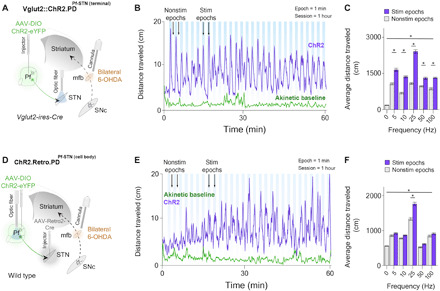
(A) An injection of AAV-DIO-ChR2 into the Pf of Vglut2 mice allowed optogenetic excitation of Pf-STN terminals via an optic fiber implanted above the STN. Bilateral 6-OHDA injections into the mfb through guide cannulae generated a bilateral PD mouse model 4 weeks after viral injection. (B) Representative example of 25-Hz excitation of Pf-STN terminals showing increased distance traveled. (C) Pf-STN terminal excitation in bilateral PD mice increased the average distance traveled compared to the akinetic baseline condition (two-way RM ANOVA, F2,60 = 0.7603, P < 0.0001, n = 5). Post hoc comparisons using Tukey’s multiple comparison test indicated that the average distance traveled during all stimulation epochs was significantly higher. (D) An injection of Retro-Cre into the STN paired with an injection of DIO-ChR2 into the Pf of wild-type mice allowed optogenetic excitation of Pf-STN cell bodies. (E) Representative example of 25-Hz optogenetic stimulation session of Pf-STN cell bodies showing increased distance traveled. (F) Pf-STN cell body excitation in bilateral PD mice significantly increased the average distance traveled compared to the akinetic baseline condition (two-way RM ANOVA, F2,60 = 86.70, P < 0.0001, n = 5).
