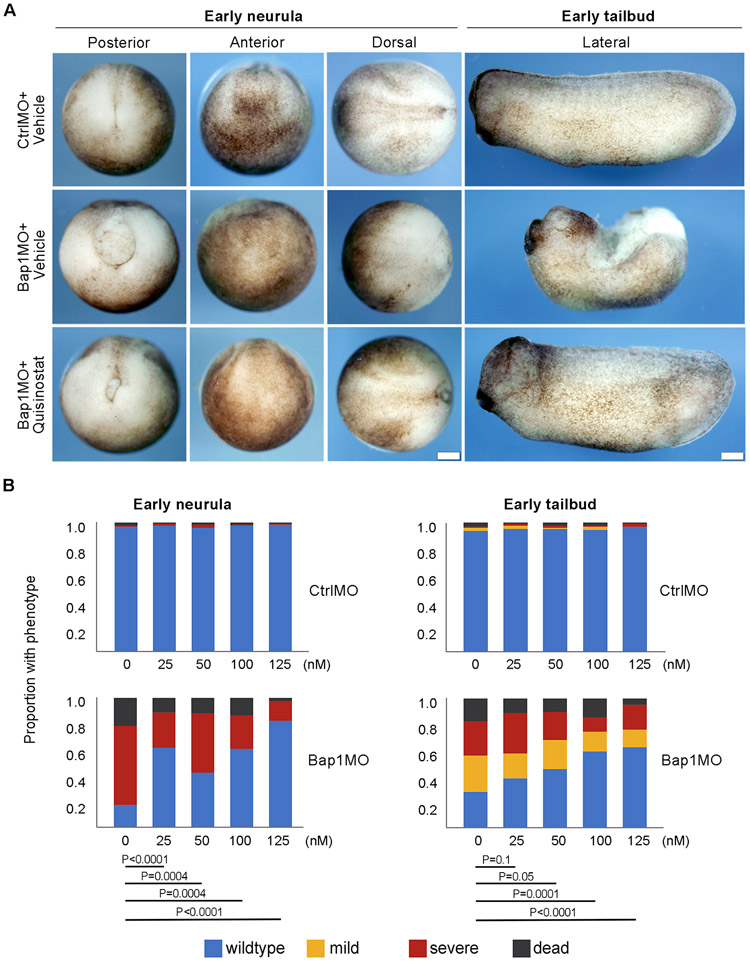
Figure 3.
Phenotypic rescue and lack of toxicity using quisinostat in Xenopus embryos. A, Representative embryos with control inactive morpholino (CtrlMO) or bap1-targeting morpholino (Bap1MO) treated with DMSO vehicle or quisinostat (125 nM) at early neurula and early tailbud stages, showing rescue of wildtype phenotype by quisinostat. Control-treated BAP1-deficient embryos showed failure of blastopore closure and elongation defect, as previously described (11). Scale bar, 250uM. B, Quantification of dose-dependent quisinostat rescue in Bap1MO-injected BAP1 deficient embryos, and lack of toxicity in CtrlMO-injected control embryos. A total of n=300 embryos from 3 different females were evaluated. P values for Bap1MO-injected embryos are indicated. None of the P values for CtrlMO-injected embryos approached statistical significance.