Figure 3. Loss of CXCR2 expression in myeloid cells inhibits tumor growth through reduced MDSC activity and enhanced activation of CD8+ T cells.
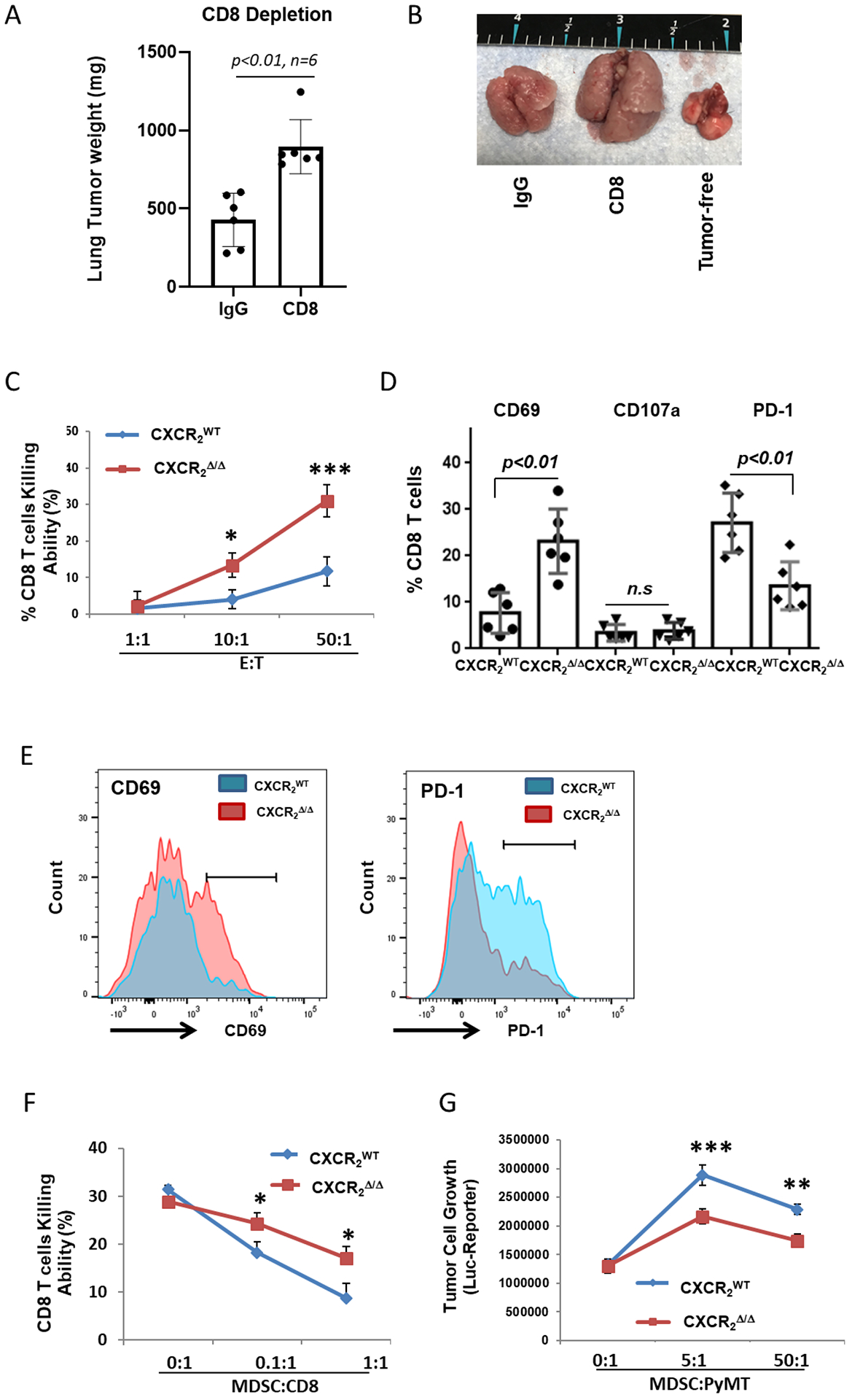
A, Tumor growth in CXCR2myeΔ/Δ mice. CXCR2myeΔ/Δ mice peritoneally treated with CD8a mAb (CD8) (n=6) or control IgG (n=6) daily for the first three days then maintained twice weekly. Three days after antibody treatment, mice were injected intravenously with 1×106 PyMT cells. Three weeks after, the mice were sacrificed, and the weight of the tumor-bearing lung was assessed. B, Representative photo of lungs from tumor-bearing mice treated with CD8 mAb or IgG control. Tumor-free lungs also shown. C, CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity ex vivo. CD8+ T cells isolated from tumor-bearing lungs of CXCR2myeΔ/Δ and CXCR2WT mice (n=3) as effector cells (E) cocultured with firefly luciferase (luc)-expressing target tumor cells (T) at the indicated E:T ratios. After 18 hours, luciferase activity in the remaining PyMT-luc cells was determined to estimate viable tumor cells and %CD8+ T-cell killing was calculated. D, MDSCs isolated from tumor-bearing lungs of CXCR2myeΔ/Δ or CXCR2WT mice (n=3) were cocultured with CD8+ T cells from lung tumor of CXCR2myeΔ/Δ or CXCR2WT mice at ratio 1:1 for 3 days and then CD8+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. E, Representative histograms of CD8+ T-cell surface markers (cells from D). F, MDSCs from tumor-bearing lungs of CXCR2myeΔ/Δ or CXCR2WT mice and CD8+ T cells from lung tumor of CXCR2myeΔ/Δ mice (n=3) at the indicated ratios were cocultured with PyMT-luc cells. After 3 days, luciferase activity was measured, and %CD8+ T-cell killing was calculated. G, MDSCs from tumor-bearing lungs of CXCR2myeΔ/Δ or CXCR2WT mice were cocultured with PyMT-luc cells at the indicated ratios. After 18 hours, luciferase activity in PyMT-luc cells was determined. Data were analyzed using the two-sample t-test with unequal variances for panels (A) and (D)(p values indicated); two-way ANOVA with a post-hoc test for panels (C), (F), and (G); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Experiments were repeated, and values represent mean±SD.
