Figure 6. CXCR2 antagonist, SX-682, inhibits tumor growth and activates CD8+ T cells.
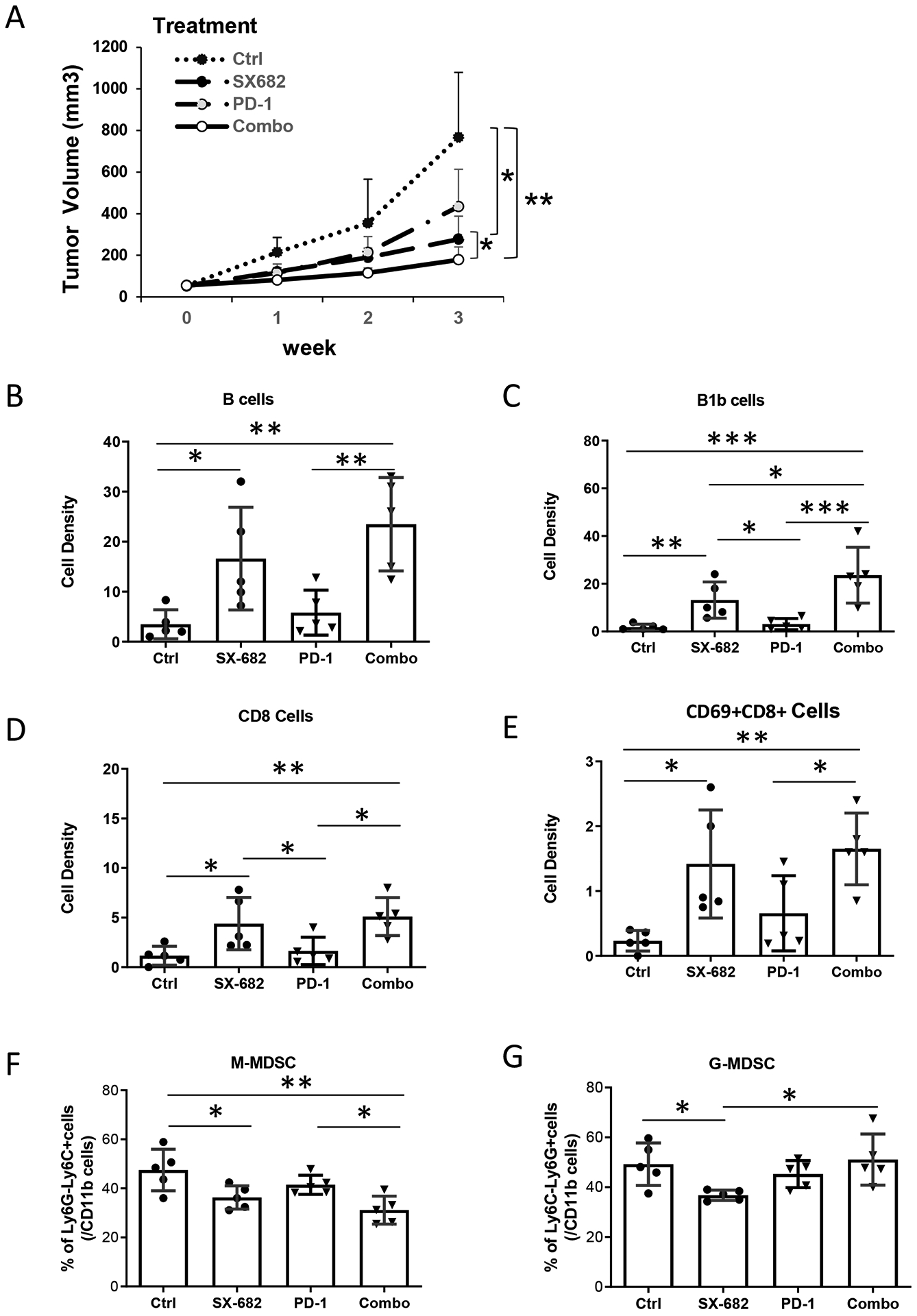
C57/BL6 mice (5 mice/group) were allowed free access to chow containing SX-682 or vehicle control from one week prior to subcutaneous implantation with Rich1.1 melanoma cells (1×106), and thereafter for the duration of the experiment. When tumor size reached 50 mm3, mice fed with SX-682 or vehicle chow were treated with or without IP injection of 100 μg anti-PD-1 or IgG isotype control every other day for a total of 26 days. A, Tumor growth was monitored weekly for three weeks. Mice were then euthanized and single-cell suspensions of tumors were prepared for flow cytometry. B, B cells (CD45+CD11b−CD19+B220+); C, B1b cells (CD19+B220+CD5−); D, CD8+ T cells (CD45+CD3+CD8+). E, Activated CD8+ T-cell (CD8+CD69+) density (cell number per mg tissue) in the TME. F, M-MDSCs or G, G-MDSC in the tumor as a percent of intratumoral CD11b+ cells. Data were plotted and analyzed by the mixed-effect model for panel (A) and by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test for panels (B-G); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Data values represent mean±SD.
