Figure 4: Cacophony and the TIR-1-like-MAPK signaling pathway promotes blockade of vesicle trafficking after nerve injury. (See also Figures S4–S6.).
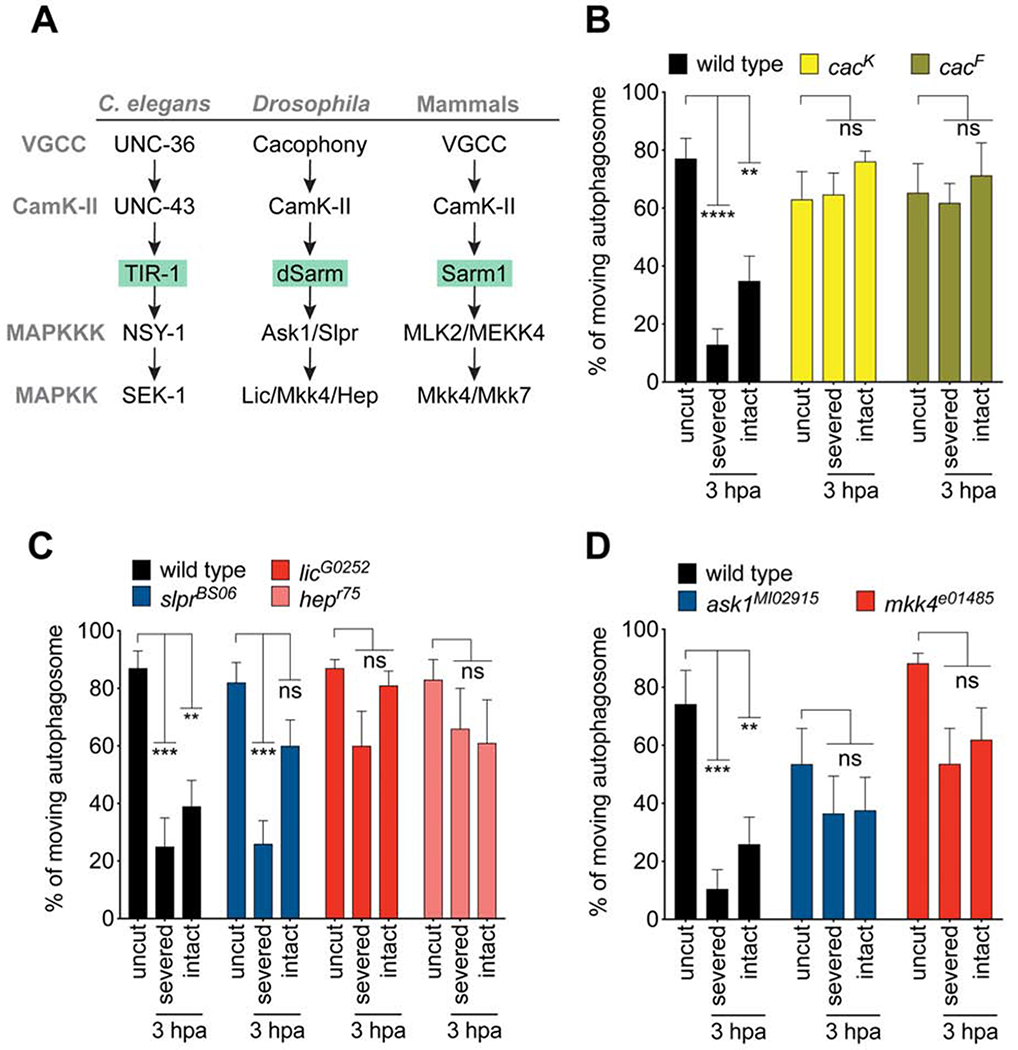
(A) The Tir-1/MAPK signaling pathway and conservation in flies and mammals. (B) Quantification of autophagosome movement in two cac mutants (cacK and cacF) in severed or proximal intact axons 3hpa compared uncut controls. (For all, Two-way ANOVA with Sidak multiple comparisons test. ns = not significant, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, n = 10 axons of each, Error bar = S.E.M.). (C) Quantification of autophagosome movement in mkk4 and askl mutants (mkk4e01485, and askMI02915) in both severed axons or proximal intact axons in injured wings (3hpa) compared to that in uninjured wings (uncut). (D) Quantification of autophagosome movement in slpr, lic, and hep mutants (slprBS06, licG0252, and hepr75) in both severed axons or proximal intact axons in injured wings (3hpa) compared to that in uninjured wings (uncut).
