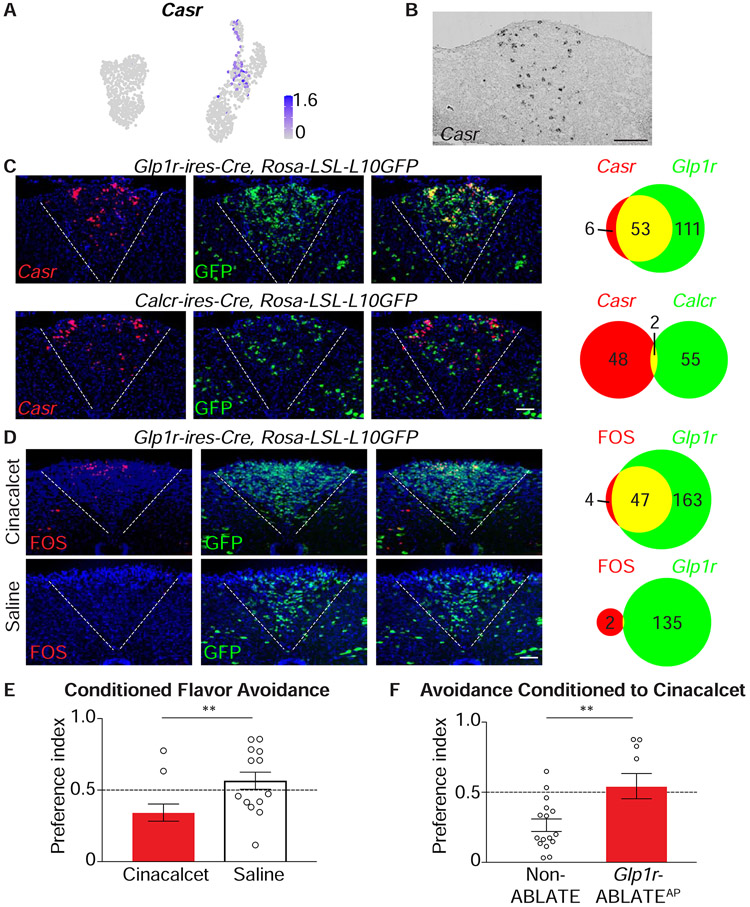
Figure 7. A neural basis for behavioral aversion conditioned by cinacalcet.
(A) UMAP plot depicting Casr expression across area postrema neurons. (B) In situ hybridization to detect Casr mRNA in coronal area postrema cryosections, scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Two-color expression analysis showing in situ hybridization to detect Casr mRNA (red) and native GFP fluorescence (green) in coronal area postrema cryosections of Glp1r-ires-Cre; Rosa26-LSL-L10GFP and Calcr-ires-Cre; Rosa26-LSL-L10GFP mice, scale bar: 100 μm. The numbers of co-labeled (yellow) or individually labeled (red, green) cells were counted (right). (D) Fos immunohistochemistry (red) and native GFP fluorescence (green) were analyzed in coronal area postrema cryosections after intraperitoneal injection of cinacalcet or saline alone in Glp1r-ires-Cre; Rosa26-LSL-L10GFP mice, scale bar: 100 μm. (E) The ability of intraperitoneal cinacalcet or saline to condition flavor avoidance was measured in wild-type mice, n=11-14, mean ± sem, circles: individual data points, **p<.01. (F) The ability of cinacalcet to condition flavor avoidance was measured in Non-ABLATE and Glp1r-ABLATEAP mice, n=10-16, mean ± sem, circles: individual data points, **p<.01.