Figure 2.
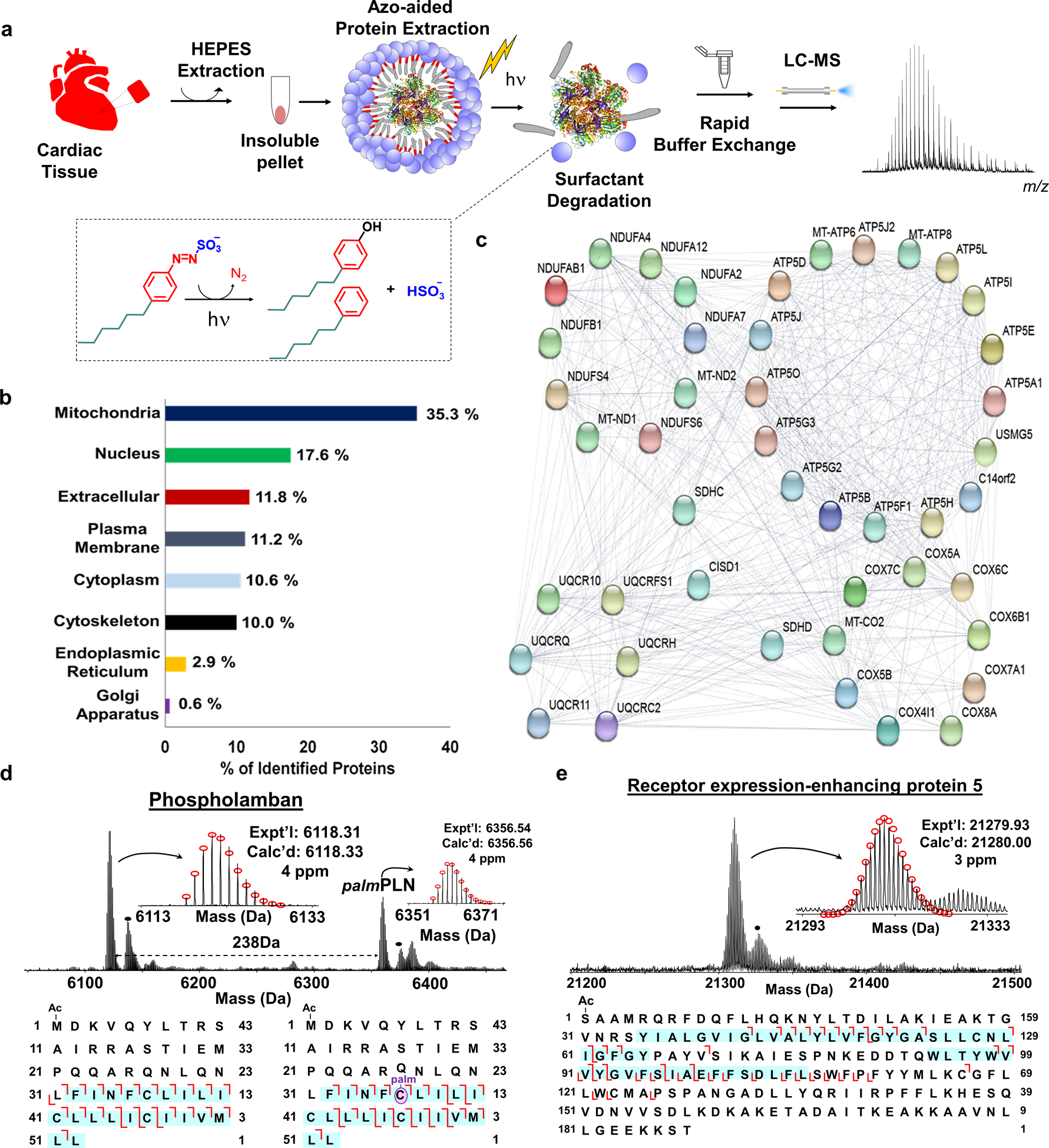
a, Scheme illustrating photocleavable surfactant (Azo)-enabled membrane proteomics. Proteins from cardiac tissue were extracted using HEPES buffer (2x) to deplete the cytosolic proteins, followed by an extraction using 0.5% Azo. The surfactant was rapid degradation (into 4-hexylphenol, 4-hexylbenzene, nitrogen, and hydrogen sulfate under UV irradiation) of the surfactant with UV irradiation (λmax = 305 nm) and buffer exchange before LC-MS analysis for proteoform characterization. Note that the molecules are not drawn to scale. b, Subcellular location of proteins identified in cardiac tissue in the Azo-aided top-down proteomics. c, Interactome map of the identified proteins with Azo that belong to the electron transport chain d-e, MS, and tandem MS analysis of representative membrane proteins. Phospholamban (PLN) and palmitoylated PLN (palmPLN) with palmitoylation localized at cysteine 36 residue (d), and receptor expression-enhancing protein 5 (e). The sequences below the spectra represent the fragmentation maps with sequence coverage and PTM localization based on online RPLC–MS/MS analysis. The regions representing the transmembrane domains are highlighted by blue shading. The dot represents +16 Da. Figure adapted from reference [31]. Copyright 2019 Springer Nature.
