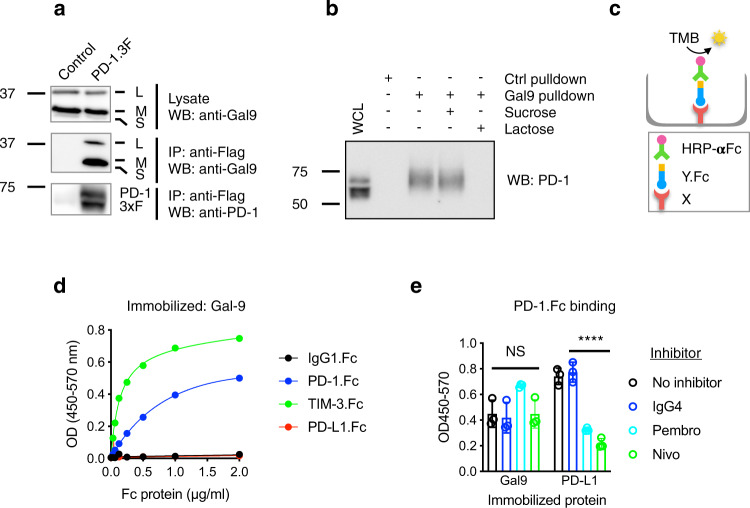
Fig. 1. Galectin-9 is a PD-1-binding protein.
a Lysates of Jurkat cells transduced with control lentivirus or PD-1 tagged at the C-terminus with 3× FLAG tag (PD-1.3F) were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG magnetic beads and the associated proteins were subjected to immunoblotting with Gal-9 or PD-1 antibodies. The three Gal-9 bands (L, M, S) represent different isoforms resulted from alternative pre-mRNA splicing. b Jurkat PD-1 cell lysates were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose (control) or Gal-9-Sepharose beads with or without sucrose or lactose. Bound proteins were eluted and western blotted with anti-PD-1 antibody. c, d Plate-based binding assay with purified recombinant proteins shows direct and specific binding of PD-1 extracellular domain (ECD) to Gal-9. MaxiSorp plates were coated with Gal-9 and incubated with Fc-fusion protein of the ECD of test binding partners (PD-1, PD-L1, or TIM-3) at various concentrations. Binding was detected by spectrophotometry using an HRP-labeled anti-human IgG (Fc-specific) antibody and the HRP substrate TMB (3,3’,5.5’-tetramethylbenzidine). X: protein immobilized on plate; Y.Fc: Fc conjugated potential binding protein or IgG1-Fc (control); HRP-αFc: HRP (horseradish peroxidase)-labeled anti-Fc antibody. e Binding of PD-1 ECD to immobilized Gal-9 or PD-L1 ECD in the absence or presence of the PD-1 antibodies pembrolizumab (Pembro) or nivolumab (Nivo). n = 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. Statistical differences were assessed using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. IgG4 vs Nivo, P < 0.0001; IgG4 vs Pembro, P < 0.0001. Data are representative of three (a, b) or two (d) independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source data file.