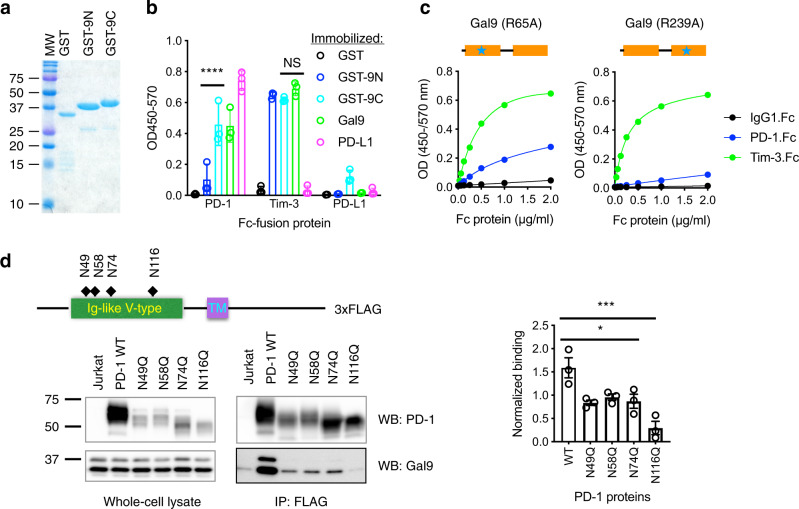
Fig. 2. Binding of Gal-9 to PD-1 is primarily mediated by the C-CRD of Gal-9 and the N116-linked glycan of PD-1.
a SDS-PAGE of GST and GST-fusion proteins of the N-CRD (GST-9N) and C-CRD (GST-9C) of Gal-9. b Plate-based binding assay measuring the binding of PD-1, TIM-3, and PD-L1 to indicated proteins immobilized on MaxiSorp plates. n = 3 independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. Statistical differences were assessed using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ****P < 0.0001. c Plate-based binding assays of PD-1 and TIM-3 binding to immobilized Gal-9 mutants with loss-of-function point mutation in the N-CRD (R65A) or C-CRD (R239A), respectively. d Lysates of Jurkat cells expressing 3xFLAG-tagged WT PD-1 or glycosylation site mutants were incubated anti-FLAG M2 magnetic beads. Bound proteins were eluted and subjected to Western blotting with PD-1 or Gal-9 antibodies. Statistical differences were assessed using ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. WT vs N49Q, P = 0.0113; WT vs N58Q, P = 0.0302; WT vs N74Q, P = 0.0148; WT vs N116Q, P = 0.0002. Data are representative of two (a, c) or three (d) experiments. Source data are provided as a Source data file.