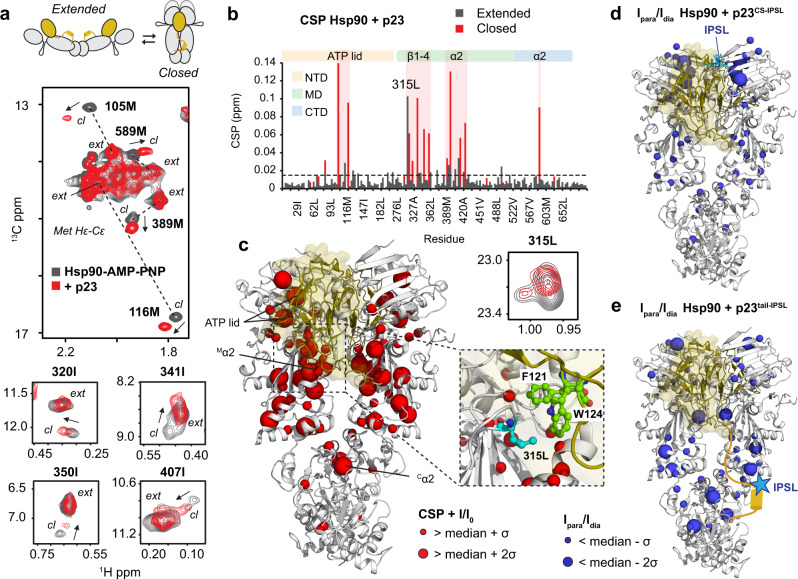
Fig. 4. NMR Analysis of the interaction of p23 with Hsp90.
a p23 triggers strong spectral changes for methyl signals in 1H-13C methyl-TROSY correlations. Top: schematic indicating open and closed conformations of the Hsp90 dimer with p23 CS and tail shown as yellow sphere and line. Middle: zoomed view of the methionine methyl region of the Hsp90-AMP–PNP spectrum in the absence (gray) and presence of 2.4 equivalents of p23 (red). Methyl signals corresponding to extended (ext) and closed (cl) conformations (in the presence of AMP–PNP) are connected by a dashed line. Chemical shift perturbations (CSP) induced by p23 binding that affect residues in the ATP lid, the helix α2 in the MD and the α2 helix projecting from the CTD are indicated by arrows. Bottom: CSPs induced by p23 binding for isoleucine methyl signals in the MD. Only the methyl signals corresponding to the closed conformation are affected by p23 binding. b CSP vs. residue number for methyl signals corresponding to extended and closed Hsp90 conformations upon binding of p23 (gray and red, respectively). Elements experiencing larger perturbations are highlighted in red and indicated at the top. c Perturbations and intensity changes are mapped onto the crystal structure of the Hsp90:p23 complex (PDB: 2CG9) as red spheres, p23 is shown in gold. A detailed view of the p23-Hsp90 interface is included on the right, indicating the most affected F121 and W124 residues of p23 (green) and L315 of Hsp90 (cyan). Zoomed view of L315 methyl resonance is shown at the top. d Intermolecular PRE of the complex with p23 spin labeled at residue 35 in the CS domain (Cys35-IPSL, cyan spheres). Residues experiencing line broadening are shown as blue spheres on the crystal structure. e PRE experiments using spin-labeled p23C35A/S189C with IPSL conjugated to residue 189 flanking the helical motif in the p23 tail. Paramagnetic effects on several MD/CTD residues (blue spheres) indicate transient interactions with the tail helix. Experiments were performed at 100 μM of Hsp90 and p23 spin labeled at 2:1 ratio corresponding to 80% of a 2:1 complex of Hsp90:p23, according to the stoichiometry obtained by ITC. Only one paramagnetic center was used for the calculations by artificially removing one p23 chain. In order to account for the different paramagnetic effects on the two protomers, the intensity ratios for protomers A and B were averaged.