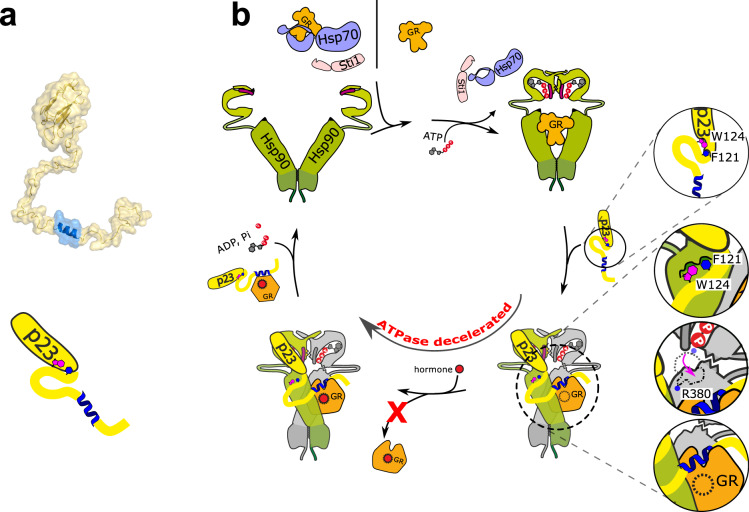
Fig. 7. Schematic model of p23 function in the Hsp90 chaperone cycle.
a. Model of p23. The p23 tail has been modeled to the CS domain of yeast p23 (PDB: 2CG9) using PyMol 1.7.1.1. The tail helix is shown in blue. A schematic model is shown at the bottom. b. The GR either binds Hsp90 directly or is recruited from Hsp70 to Hsp90 via the adapter co-chaperone Sti1/Hop. PPIases compete with Sti1/Hop for Hsp90 binding and displace Sti1/Hop (not shown). In free p23, the W124 and F121 residues contact the core domain (1st inset). Upon binding to the ATP-bound, closed Hsp90 conformation, these aromatic residues bind a hydrophobic pocket on the Hsp90 middle domain (2nd inset). The inhibitory effect of p23 on the Hsp90 ATPase is caused by a shift of the catalytic loop conformation, which positions the R380 residue in a way that prevents ATP hydrolysis (3rd inset). The C-terminal tail of p23 contains a helical segment, which interacts and stabilizes Hsp90-bound GR and prevents premature dissociation of the GR from Hsp90 (4th inset).