FIGURE 6.
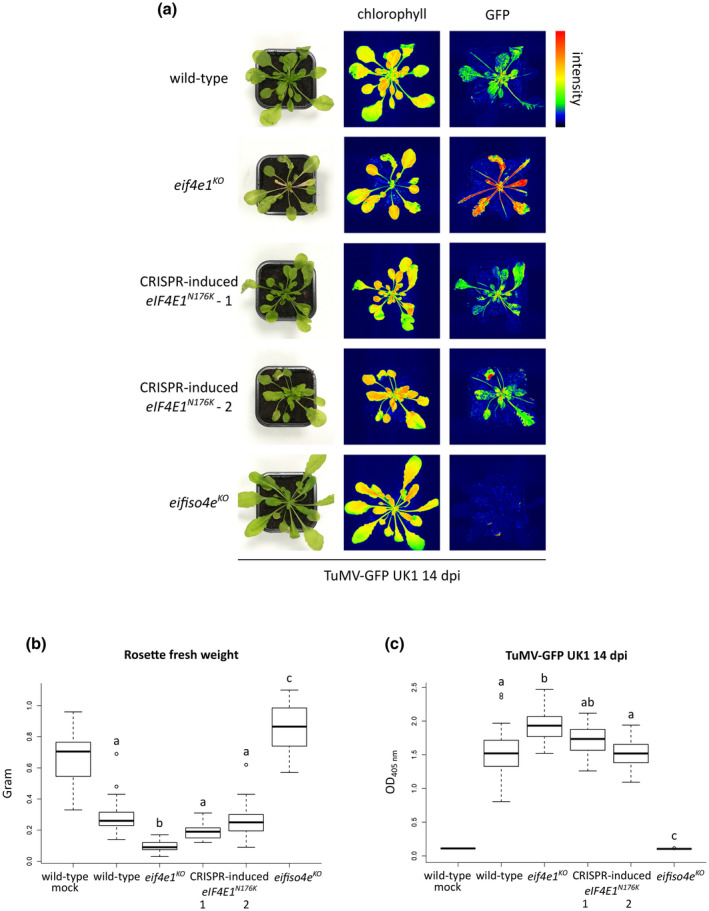
The functional eIF4E1N176K resistance allele does not trigger hypersusceptibility to turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). (a) Phenotypic comparison of representative plants upon TuMV‐GFP UK1 infection at 14 days postinoculation (dpi). Photographs were taken under natural light conditions (left panel) and under wavelengths specific for chlorophyll excitation (middle panel) or green fluorescent protein (GFP) excitation (right panel) by using GFP Camera (PSI) fluorescence imaging. Fluorescence is represented by false colours ranging from blue (low intensity) to red (high intensity). Two independently obtained CRISPR‐induced eIF4E1N176K lines were used in the analyses. (b) Rosette fresh weight analysis of plants inoculated with TuMV‐GFP UK1 at 18 dpi. The aerial part was weighed for 24 wild‐type mock‐inoculated plants and at least 23 TuMV‐GFP UK1‐inoculated plants of each genotype. (c) Accumulation analysis of TuMV‐GFP UK1 at 14 dpi. Viral accumulation was detected by double antibody sandwich‐ELISA for TuMV coat protein (CP) on 24 mock‐inoculated and 24 TuMV‐GFP UK1‐inoculated plants of each genotype. Different letters depict significantly different groups identified by Kruskal–Wallis statistical tests at p < .05
