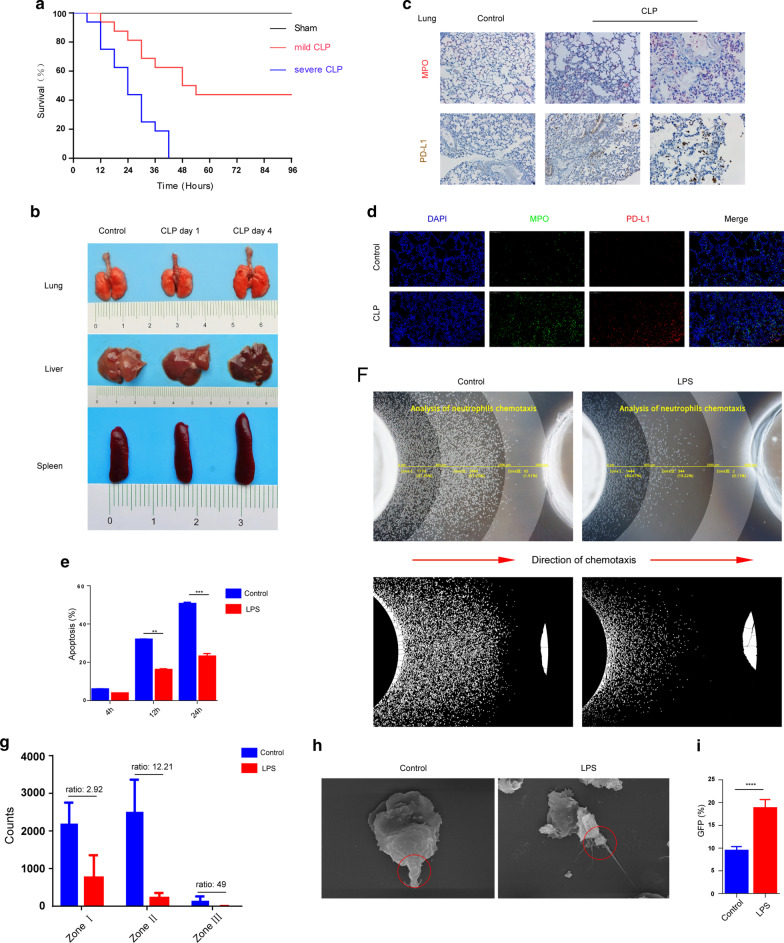
Fig. 1.
Sepsis results in neutrophil function challenge and increasing in neutrophil expression of PD-L1. a Survival rate change in CLP mouse model of sepsis. C57BL6/J mice with CLP-induced sepsis were randomized in three groups: sham (n = 12), severe CLP group (n = 16) and mild CLP group (n = 16). b Lung, liver and spleen pictographs from sham animals (control) and animals challenged with cecal-ligation and puncture (CLP). c, d Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence changes in lung sections of CLP (96 h) sepsis mouse model. In the immunohistochemistry, MPO was marked in red and PD-L1 expressing was marked in brown. In immunofluorescence, DAPI showed the cell nucleus in light blue, MPO marked the neutrophils in green, and PD-L1 expressing was marked in red. e Changes in mouse neutrophil apoptosis result after LPS stimulation (n = 5). f–g Neutrophil chemotaxis toward fMLP was assayed (n = 6). h Scanning electron microscopy showed shape change of neutrophils after LPS stimulation. The red circles represent the posterior tails of polarized neutrophils. i Changes in neutrophil phagocytosis in mice after LPS stimulation (n = 5). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Data are mean ± SEM