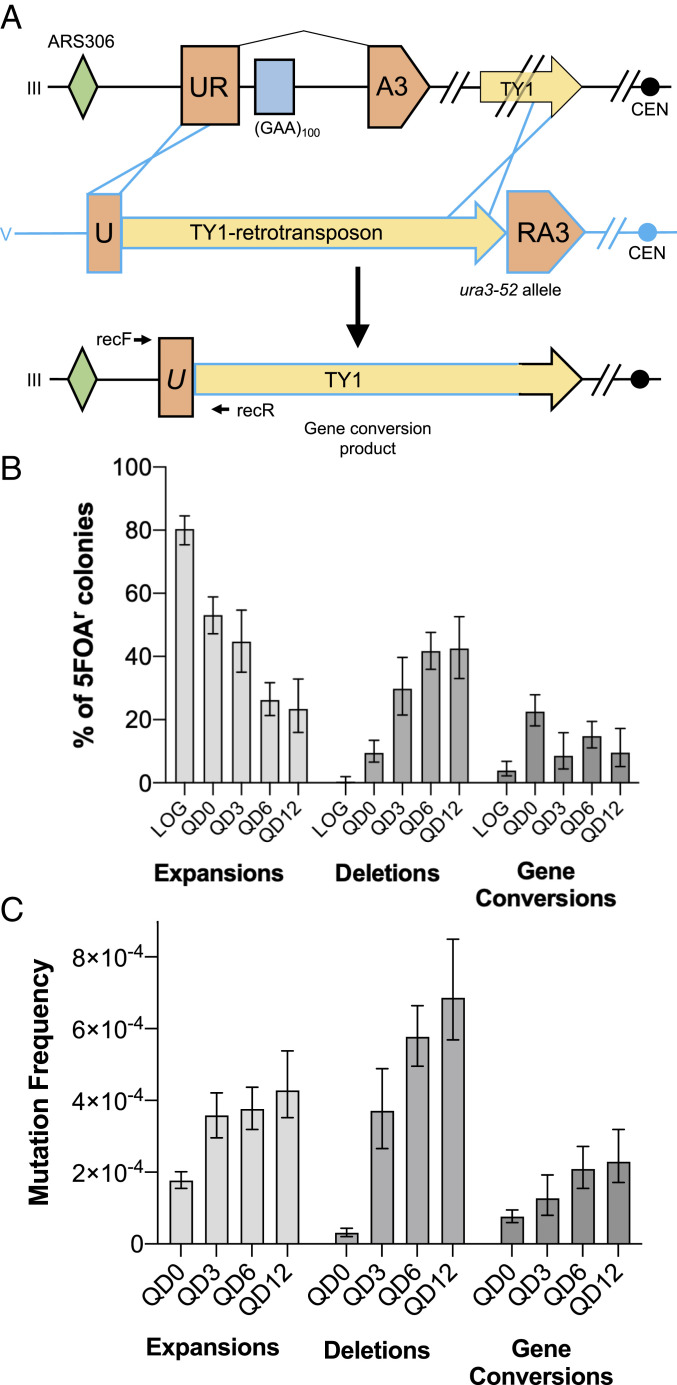
Fig. 2.
The predominant (GAA)n-mediated mutation in quiescence is large-scale deletions, but all mutation types increase throughout quiescence. (A) Schematic of previous long-read sequencing assessment of gene conversion events (46). Recombination occurs via homology between our artificial URA3-containing construct on Chr III (black) and the ura3-52 allele on Chr V (blue). Yellow arrows represent paralogous Ty-1 retrotransposable elements. RecF/R: primers to detect gene conversion events. (B) Percentage of 5-FOA–resistant colonies demonstrating each of the mutation types interrogated during logarithmic growth and quiescence. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals calculated via the Wilson method. (C) Bars represent median mutation frequency across time points during chronological aging. Error bars represent 95% credible intervals from our model for estimating mutation frequency distributions via Bayesian logistic regression.