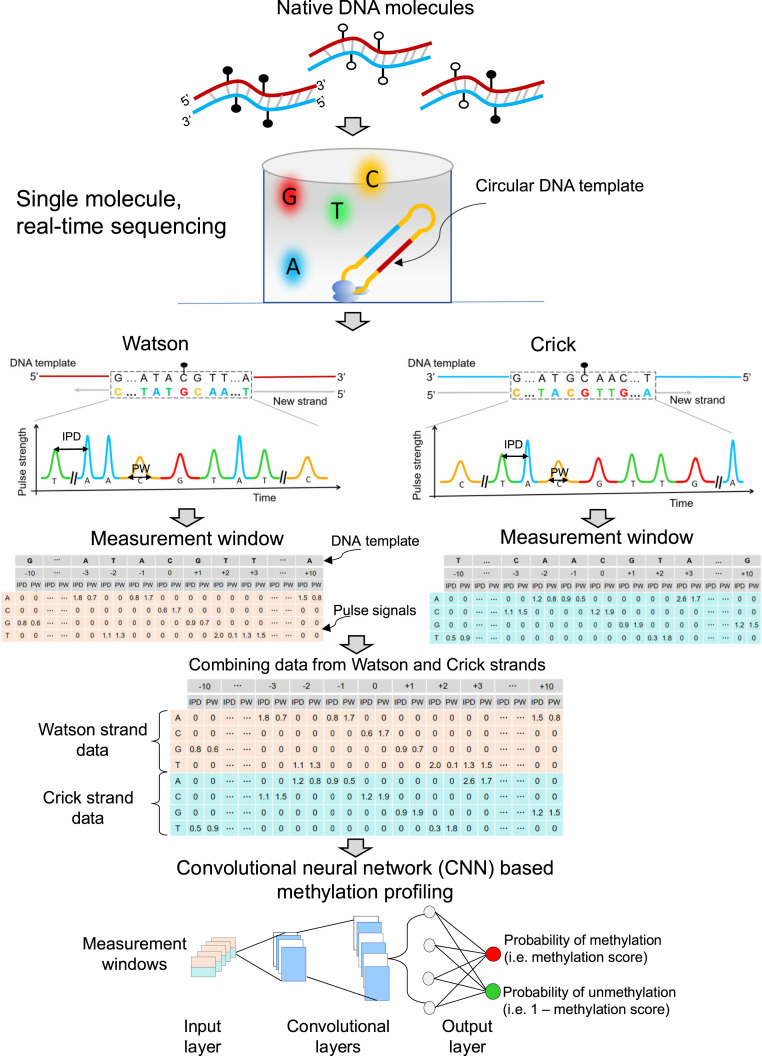
Fig. 1.
Schematic 5mC detection using single molecule sequencing and the HK model. Double-stranded DNA molecules were ligated with hairpin adapters, forming circular DNA templates. DNA polymerase in a ZMW would incorporate nucleotides labeled with different fluorophores into the complementary strand of a DNA template, thus emitting different fluorescent colors indicating nucleotide information: for example, red, yellow, green, and blue colors represented G, C, T, and A, respectively. The light pulse signals were reflective of DNA polymerase kinetics, depending on the base modifications. Pulse signals included IPD and PW. For a cytosine subjected to methylation analysis, IPDs, PWs, and sequence context surrounding that cytosine were organized into a data matrix, referred to as a measurement window. For illustration purposes, the 10 nt upstream and downstream of the cytosine within a CpG site in question were presented as 5′-G[CCATGC]ATACGTT[GATGCA]A-3′ for the Watson strand. The bases in the brackets were left out (denoted by “…”) for the sake of simplicity. In this case, the measurement window size, including the interrogated cytosine in the middle, was 21 nt. For a position of -3 corresponding to the base of adenine (“A”), the IPD (1.8) and PW (0.7) associated with “A” were filled in the corresponding cells between a column of “-3” and a row of “A.” The other cells in the same columns were filled by “0.” The remaining IPDs and PWs related to the 21-nt sequence context were filled in that measurement window based on the same rule. The kinetic signals and sequence context originating from the Crick strand (‘5-T[TTGCAT]CAACGTA[TGCATG]G-3′) were also processed similarly. The measurement windows for two CpG sites complementary to each other (i.e., the Watson strand and the Crick strand) were combined for downstream analysis. A number of combined measurement windows originating from methylated and unmethylated cytosines were used for training a CNN, so as to differentiate methylated and unmethylated cytosines in test samples. CNN involved input layer, convolutional layers, and output layer. The measurement windows were fed into the input layer, followed by the process of convolutional layers; then, the probability of methylation (range: 0 to 1) for a CpG was generated through the output layer based on a sigmoid function. This approach was referred to as the “holistic kinetic (HK) model” (HK model).