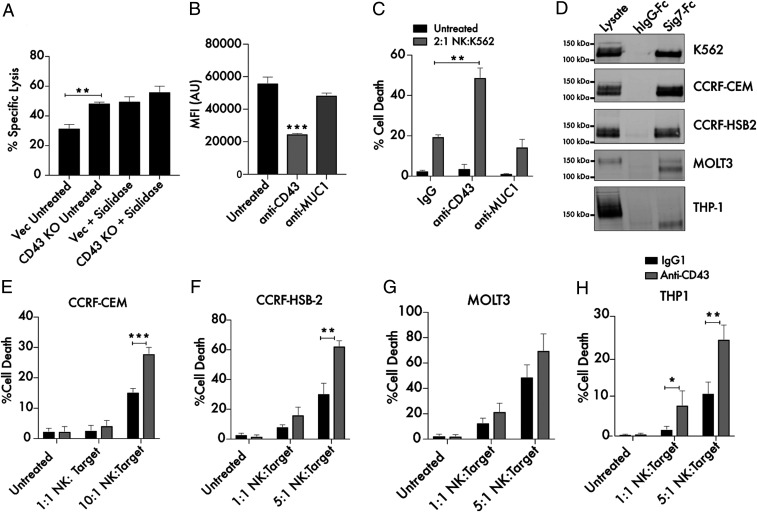
Fig. 6.
Targeting CD43 enhances killing of leukemia cells by primary NK cells. (A) Primary NK cells and K562 Vec (empty vector transfected) or CD43 KO target cells were cocultured for 4 h at a 2:1 ratio and subjected to flow cytometry using live cell (CellTrace Far Red) and dead cell (Sytox Green) stains to quantitate specific lysis of the target cells. The experiment was also performed following treatment of both Vec and KO target cells with 2 μM endotoxin-free sialidase from Salmonella Typhimurium. (B) A total of 104 K562 cells were treated with 10 μg/mL anti-CD43 (MEM-59) or anti-Muc1 (VU4H5) antibodies for 30 min, incubated with 100 ng/mL Siglec-7–Fc/Alexa Fluor 488, and subjected to flow cytometry. MFI indicates mean fluorescence intensity, and AU indicates arbitrary units. (C) K562 cells were treated for 30 min with 10 μg/mL isotype control, anti-CD43, and anti-MUC1 antibodies. Cells were then cocultured with primary NK cells at the indicated ratio as in A. The “Untreated” condition refers to target cells that have not been incubated with NK cells. (D) Lysates from the indicated leukemia and lymphoma cell lines were passed over Siglec-7–Fc functionalized beads. Bound proteins were eluted from the beads and subjected to Western blot to assess the presence of a Siglec-7–binding CD43 glycoform. Beads conjugated to huFc were used as a control. A total of 25 μg protein was loaded in the input lysate, while 500 μg protein was used for each IP. (E) CCRF-CEM cells, (F) CCRF-HSB2 cells, (G) MOLT3 cells, and (H) THP-1 cells were treated for 30 min with 10 μg/mL isotype control or anti-CD43 mouse IgG1 antibody and cocultured with primary NK cells at the indicated ratios as in A. n = 3 in all cases. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM.