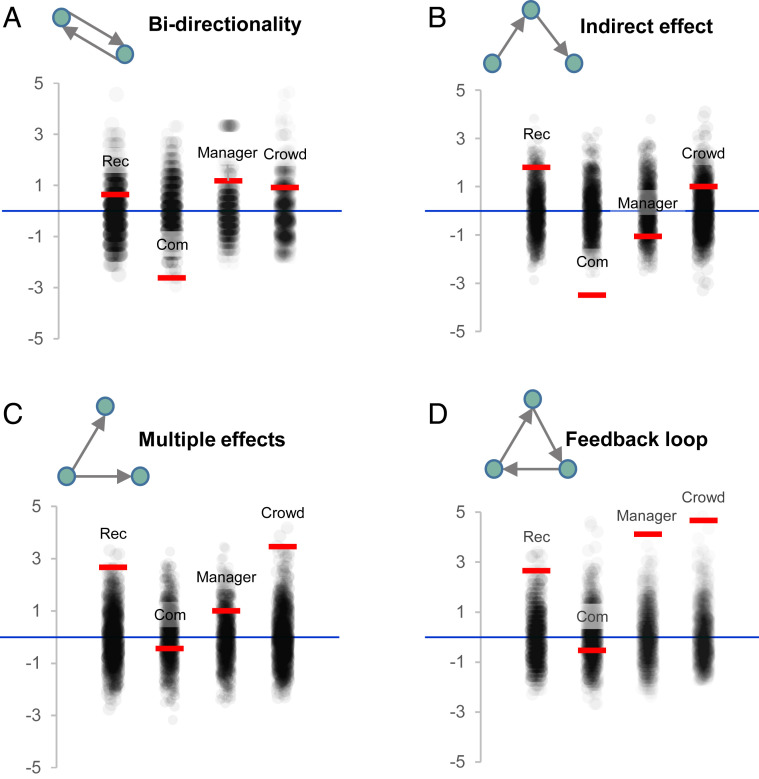
Fig. 3.
Deviation of the prevalence of complex causal motifs in aggregated models relative to uniform random graphs for bidirectionality (A), indirect effect (B), multiple effects (C), and feedback loops (D). Black dots represent 10,000 random graphs, and the blue line shows the expected value of motif counts. Red dashes represent the deviation of each model from the expected value.