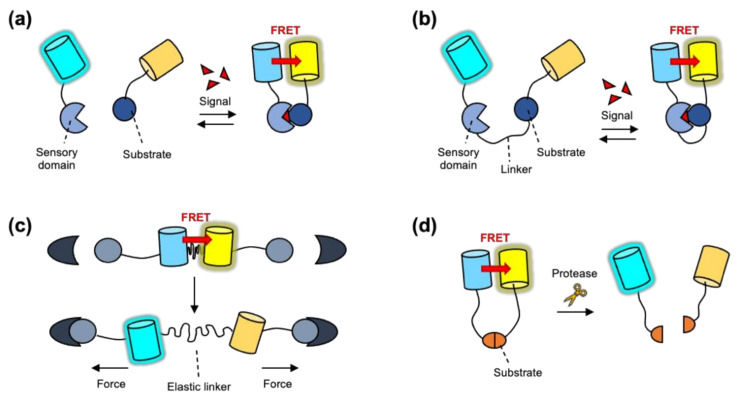
Figure 2.
Designs of FRET biosensors (a) Representative design of an intermolecular FRET biosensor. The signal-induced interaction of the modified substrate and the sensory domain results in the increase of FRET between donor and acceptor FP. (b) Representative design of an intramolecular FRET biosensor. The signal-induced conformational change of the biosensor increases the FRET level. (c) Design of a FRET-based tension sensor. Its FRET level is designed to decrease by the applied tensional force. (d) Design of a FRET-based protease sensor. The activated protease cleaves its substrate, resulting in the decreased FRET of the biosensor.