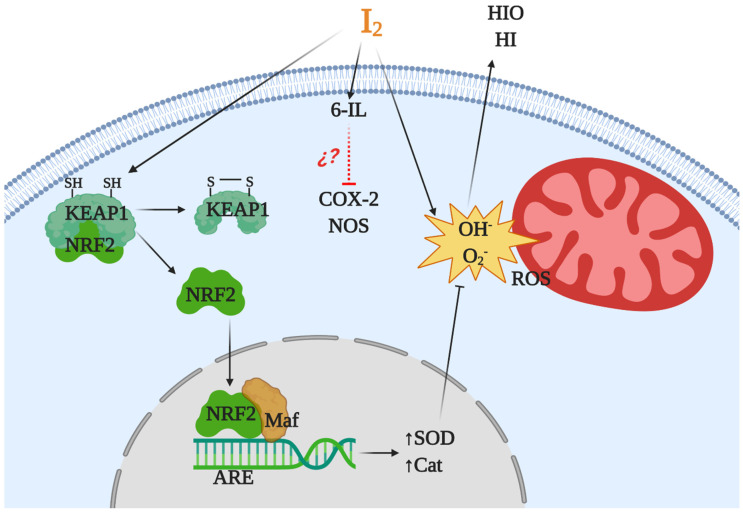
Figure 2.
Antioxidant mechanisms of molecular iodine (I2). I2 acts as a scavenger of a reactive oxygen species (ROS) like hydroxyl radicals (OH) or superoxide anions (O2) generating neutral components hypoiodous acid (HIO) or hydroiodic acid (HI). I2 in combination with arachidonic acid (AA), and generating the iodolipid 6-iodolactone (6-IL), inhibits the activity of proinflammatory enzymes like nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cyclooxygenase type 2 (Cox2). In addition, the iodination of the cysteine-rich protein Keap1 releases and promotes the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) that with Maf activates the antioxidant response element (ARE), inducing overexpression of antioxidant enzymes type II like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (Cat).