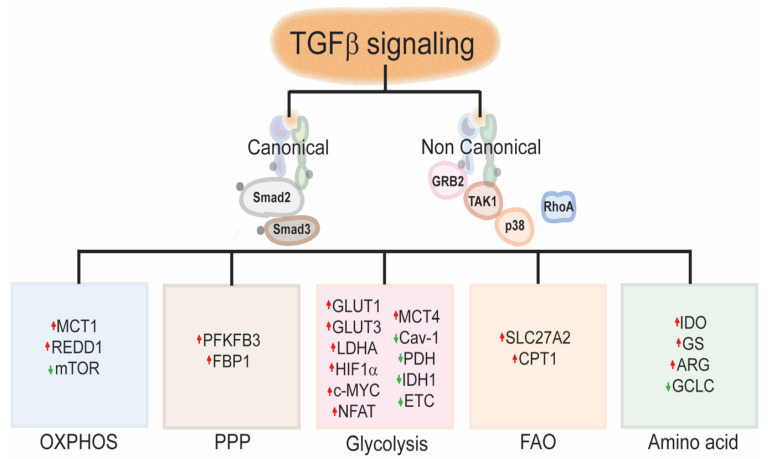
Figure 1.
TGF-β signaling and metabolic reprograming: TGF-β canonical and non-canonical signaling activation promotes the metabolic skewing to either glycolytic or oxidative metabolism in the TME by modulating the transcription of genes involved in glycolysis, OXPHOS, PPP, FAO or amino acid metabolism, directly or indirectly (see text.) TGFβ, Transforming Growth factor beta; GRB2, Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; TAK1, Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases; RhoA, Ras homolog family member A; MCT1, Monocarboxylate transporter 1; MCT4, Monocarboxylate transporter 4; REDD1, Regulated in development and DNA damage response 1; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; PFKFB3, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; FBP1, Fructose-1,6-biphosphatase, GLUT1, Glucose transporter 1; GLUT3, Glucose transporter 3; LDHA, Lactate dehydrogenase A; HIF1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; c-MYC, MYC proto-oncogene BHLH Transcription factor; NFAT; Nuclear factor of activated T-cells; Cav-1, Caveolin 1; PDH Pyruvate dehydrogenase; IDH1, Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; ETC, Electron transport chain; SLC27A2, solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 2; IDO, Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; GS; Glutamine synthetase; ARG, Arginase; GCLC, Glutamate-cysteine Ligase catalytic subunit; OXPHOS, Oxidative phosphorylation; PPP, Pentose Phosphate Pathway; FAO, Fatty acid oxidation.