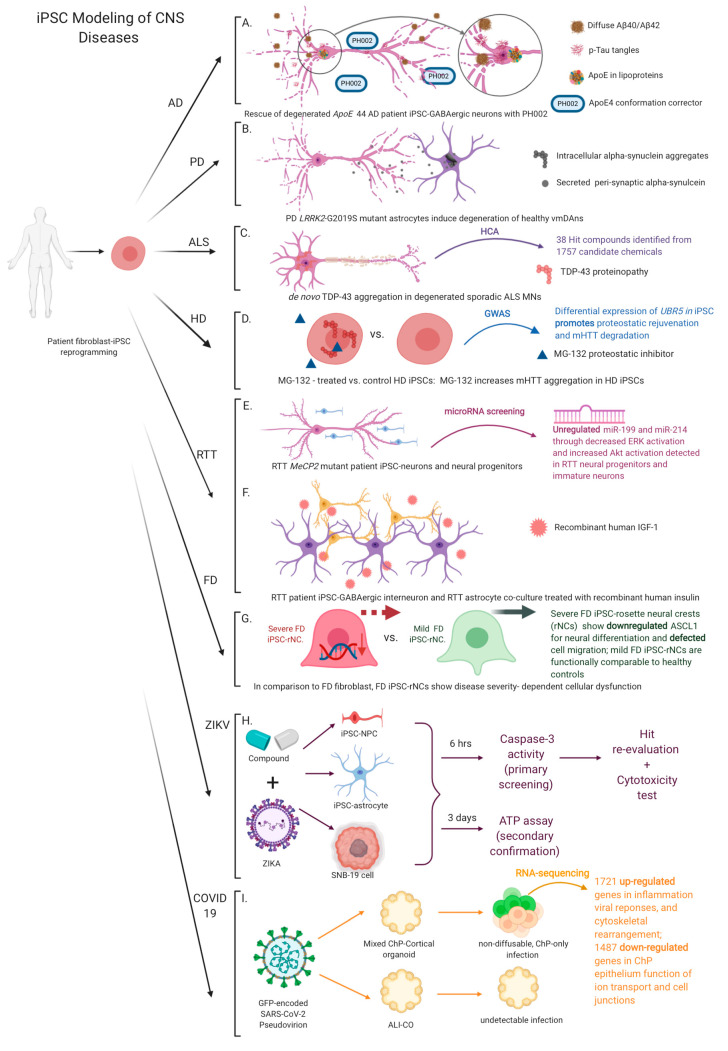
Figure 2.
iPSC modeling of diverse CNS diseases for phenotype studies and drug discovery. (A) A proof-of-concept experiment to conformationally correct APOE4 in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) with the compound PH002. PH002 improves cytopathologies of APOE 44 human iPSC-GABAergic neurons with reduced p-tau accumulation, Aβ40/Aβ42 production/secretion, and ApoE4 fragments. (B) A co-culture model of astrocytes and ventral midbrain dopaminergic neurons (vmDAns) derived from Parkinson’s disease (PD) patient-specific iPSCs carrying LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Co-culture of LRRK2 G2019S astrocytes with healthy vmDAns induces α-syn toxicity and vmDAns neuron degeneration as observed in PD patient brains. (C) Model of de novo TDP-43 proteinopathy and motor neuron (MN) degeneration in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patient iPSC-MNs. Automated robotics is applied on a high-content assay to screen against 1757 bioactive compounds. Based on the evaluation of reduced TDP-43 aggregation, 38 hit compounds are identified to effectively reduce the percent cells containing TDP-43 aggregates. (D) Utilize Huntington’s disease (HD) iPSCs as a model to study reprogramming-associated anti-mHTT aggregation compared to aggregate-free HD iPSCs. Treatment of the proteasomal inhibitor MG-132 increases mHTT aggregates in HD iPSCs, indicating a correlation between anti-mHTT aggregation and proteasomal homeostasis. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) analysis shows upregulation of UBR5 particularly at the iPSC stage, which rejuvenates the proteasomal function of HD iPSCs to actively degrade mHTT aggregates. UBR5 thus serves as a potential therapeutic target to remove mHTT aggregation in HD patient cells. (E) Generation of neural progenitors and immature neurons from isogenic Rett syndrome (RTT) patient iPSCs to model MeCP2 mutation-associated neurogenic deficiency during the early brain development. In comparison with the healthy control, MeCP2 mutant neural progenitors and neurons show upregulated microRNA miR-199 and miR-214 in microRNA screening. Molecularly, immunoblots show decreased ERK activation and increased AKT activation, implicating a possibility of delayed neuron differentiation. (F) Treatment of recombinant human IGF-1 to improve neural performance in RTT. RTT iPSC-astrocytes are found to reduce the amount of terminal ends of RTT iPSC-GABAergic interneurons in co-culture. Short-term administration of IGF-1 modestly improves the neurite length of RTT-neurons in a diseased environment. (G) Model familial dysautonomia (FD) of various disease severities with FD iPSC-rosette neural crests (rNCs). In comparison to a healthy control, mild FD rNCs do not display differences in cell migration or the expression level of ASCL1, a proneural transcriptional factor for early neurogenesis and progenitor differentiation. In contrast, severe FD rNCs show compromised cell motility and decreased ASCL1 expression, indicating a disease severity-dependent functional defect that might shape the accuracy of disease modeling. (H) Compound screen flow chart for ZIKV therapy development. Three different cell types are used as a platform for drug screen: iPSC-neural progenitor, iPSC-astrocytes, and glioblastoma cell (SNB-19). SNB-19 and neural progenitors are exposed to ZIKV infection and screened against compounds that reduce apoptotic caspase-3 activity. The derived primary hits are re-evaluated on all cell types along with cytotoxicity assay. ATP assay is used as secondary confirmation of post-infection cell survival. (I) Utilize human iPSC-Choroid plexus (ChP) and cortical organoids to investigate neurotropism in SARS-CoV-2 infection. GFP-encoded pseudovirion is made to intracellularly visualize viral invasion. When cortical organoids mixed with ChP cells are exposed to the virus, only ChP cells but not neural progenitors or neurons show positive infection signals; infection does not spread to nearby cortical regions but infected ChP cells lead to global transcriptomic dysregulations in multiple cellular functions (top). When air–liquid-interface cerebral organoids (ALI-COs) are introduced with greater neuronal maturity to examine the viral infection in neurons, signal is undetectable relative to the positive control, evidencing a preferred attack on ChP cells and a lack of viral entry in neural cells (bottom).