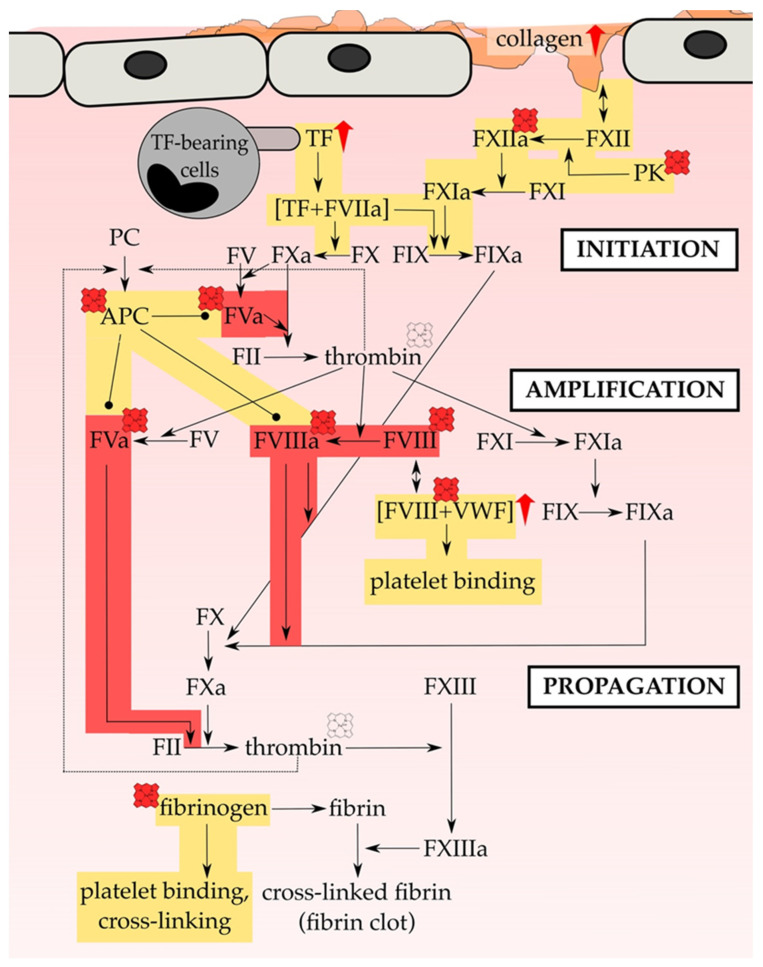
Figure 4.
Heme promotes plasmatic hemostasis. Heme can directly affect various proteins of the blood coagulation cascade. While usually activated through the exposure of TF (e.g., by monocytes or the subendothelium), in pathologic thrombotic situations hemostasis activation through the exposure of negatively charged surfaces (e.g., of collagen) plays a supportive role. Indeed, initiation, amplification and propagation of hemostasis on the surface of cells (TF-bearing cells and platelets) is targeted by heme, either through upregulation of proteins’ expression level (red arrow) or regulation of proteins’ function (heme symbol). Direct heme-binding with functional consequences was only demonstrated for APC, FVIII(a) and fibrinogen. Contradictory results were obtained in case of the impact of heme on the activity of thrombin (pale heme symbol). The investigations of more than 35 years research allow for the assumption that heme is able to initiate hemostasis via both the upregulation of TF expression on leukocytes and endothelial cells as well as of collagen in the subendothelium. Most of the analyzed interactions tend to a procoagulant/prothrombotic (yellow) impact of heme. In contrast, heme-induced FVIIIa and FVa inactivation is exclusively described leading to anticoagulant (red) consequences. FVIII and FV are central cofactors of the coagulation cascade. Thus, the inactivation of FVIIIa and FVa by heme could constitute kind of a control center of heme-mediated initiation, amplification and propagation of the coagulation process. Plasma level changes of clotting factors that were recorded in humans upon heme infusion are not included. APC = activated protein C, FIIa = thrombin, FII = prothrombin, FV = factor V, FVa = activated factor V, FVIIa = activated factor VII, FVIII = factor VIII, FVIIIa = activated factor VIII, FIX = factor IX, FIXa = activated FIX, FX = factor X, FXa = activated FX, FXI = factor XI, FXIa = activated FXI, FXII = factor FXII, FXIIa = activated factor XII, FXIII = factor XIII, FXIIIa = activated factor XIII, PC = protein C, PK = plasma kallikrein, VWF = von Willebrand factor.